Legacy Document
Important: The information in this document is obsolete and should not be used for new development.
Important: The information in this document is obsolete and should not be used for new development.
tan
You can use thetanfunction to compute the tangent of a real number.
double_t tan (double_t x);
x- Any finite floating-point number.
DESCRIPTION
Thetanfunction returns the tangent of its argument. The argument is the measure of an angle expressed in radians. This function is antisymmetric.The
atanfunction performs the inverse operation .EXCEPTIONS
When x is finite and nonzero, the result of might raise one of the following exceptions:
- inexact (for all finite, nonzero values of x)
- underflow (if the result is inexact and must be represented as a denormalized number or 0)
SPECIAL CASES
Table 10-22 shows the results when the argument to thetanfunction is a zero, a NaN, or an Infinity, plus other special cases for thetanfunction.
Special cases for the tanfunctionOperation Result Exceptions raised 0 Inexact + 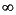
Inexact +0 None None NaN None[43] NaN Invalid NaN Invalid EXAMPLES
z = tan(pi); /* z = 0. The inexact exception is raised. */ z = tan(pi/2); /* z = +INFINITY. The inexact exception is raised. */ z = tan(pi/4); /* z = 1. The inexact exception is raised. */
[43] If the NaN is a signaling NaN, the invalid exception is raised.