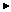 New in Project to add another class.
New in Project to add another class.
import next.util.*;
import next.wo.*;
public class Person extends Object {
ImmutableHashtable personRecord;
public Person(ImmutableHashtable personDict) {
super();
personRecord = personDict;
}
}
Person initializes the personRecord instance variable using a dictionary returned by the Main component of the Registration application.
public ImmutableHashtable validate() {
MutableHashtable valid = new MutableHashtable();
if ((((String)(personRecord.get("address"))).length() == 0) &&
(((String)(personRecord.get("name"))).length() == 0)) {
valid.put("failureReason",
"You must supply a name and address");
valid.put("valid", "No");
} else if (((String)(personRecord.get("name"))).length()
== 0) {
valid.put("failureReason", "You must supply a name.");
valid.put("valid", "No");
} else if (((String)(personRecord.get("address"))).length()
== 0) {
valid.put("failureReason",
"You must supply an address");
valid.put("valid", "No");
} else {
valid.put("valid", "Yes");
}
return valid;
}
Person's validate method checks whether the data entered by the user includes values for a name and address. The validate method returns a dictionary. This dictionary contains a status message and a validation flag that indicates whether the registration should be allowed to proceed. If the user failed to enter a name or address, the validation flag value is "No," which disallows the registration. The status message then prompts the user to supply the missing information.
public String name() {
return (String)(personRecord.get("name"));
}
public ImmutableHashtable personAsDictionary() {
return personRecord;
}
The name method is simply used to return the Person's name, while the method personAsDictionary returns a dictionary representation of the Person. The dictionary representation is used when the Person's data is written out to a file in a property list format (in RegistrationManager's writeRegistrantsToFile method).
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents  Previous Section
Previous Section
 Next Section
Next Section