Mapping Overview
This article provides an overview of the mapping model.
In order to transform data from one version of a schema to another, you need a definition of how to perform the transformation. In Core Data, this information is captured in a mapping model. A mapping model is a collection of objects that specifies the transformations that are required to migrate part of a store from one version of your model to another (for example, that one entity is renamed, an attribute is added to another, and a third split into two).
You typically create a mapping model in Xcode. Much as the managed object model editor allows you to graphically create the model, the mapping model editor allows you to customize the mappings between the source and destination entities and properties.
Contents:
Mapping Model Objects
Creating a Mapping Model in Xcode
Mapping Model Objects
Like a managed object model, a mapping model is a collection of objects. Mapping model classes parallel the managed object model classes—there are mapping classes for a model, an entity, and a property (NSMappingModel, NSEntityMapping, and NSPropertyMapping respectively).
An instance of
NSEntityMappingspecifies a source entity, a destination entity (the type of object to create to correspond to the source object) and mapping type (add, remove, copy as is, or transform).An instance of
NSPropertyMappingspecifies the name of the property in the source and in the destination entity, and a value expression to create the value for the destination property.
The model does not contain instances of NSEntityMigrationPolicy or any of its subclasses, however amongst other attributes instance of NSEntityMapping can specify the name of an entity migration policy class (a subclass of NSEntityMigrationPolicy) to use to customize the migration. For more about entity migration policy classes, see “Custom Entity Migration Policies .”
Creating a Mapping Model in Xcode
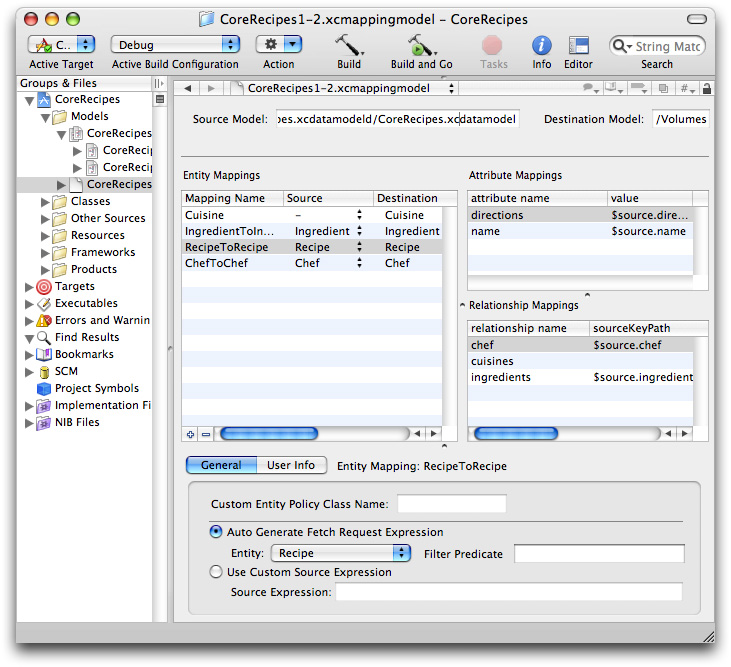
From the File menu, you select New File and in the New File pane select Design > Mapping Model. In the following pane, you select the source and destination models. When you click Finish, Xcode creates a new mapping model that contains as many default mappings as it can deduce from the source and destination. For example, given the model files shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, Xcode creates a mapping model as shown in Figure 1.
Reserved words in custom value expressions: If you use a custom value expression, you must escape reserved words such as SIZE, FIRST, and LAST using a # (for example, $source.#size).
© 2008 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. (Last updated: 2008-02-08)