Expansion Features
This chapter describes the expansion features of the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer’s RAM expansion slots and the CardBus slot.
In this section:
RAM Expansion Slots
CardBus Slot
RAM Expansion Slots
The computer has two RAM expansion slots that accommodate standard SO (small outline) DIMMs using DDR SDRAM devices. One slot may is occupied by factory-installed SO-DIMM. The slots are accessible for user installation of an additional SO-DIMM.
The SO-DIMMs must use DDR SDRAM devices. If the user installs an SO-DIMM that uses Single Data Rate (SDR) devices, the boot process will fail when the user attempts to restart the computer and the computer will not operate.
The address logic for the RAM slots supports up to 1 GB total RAM. Using the highest-density devices currently available, an SO-DIMM can contain up to 512 MB of RAM, so the two RAM expansion slots can accommodate up to 1 GB total RAM.
Accessing the RAM Slots
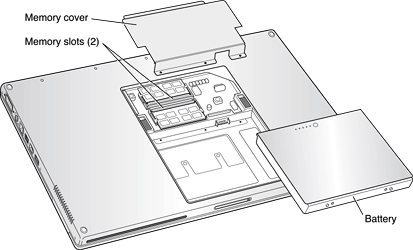
The user can access the RAM expansion slots by removing the memory slot cover on the back of the computer, as shown in Figure 4-1. For complete instructions on accessing and replacing the RAM memory, refer to the PowerBook G4 17-inch Getting Started guide that came with the computer.
Mechanical Design of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs
The RAM expansion modules used in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer are PC2700 DDR333 RAM SO-DIMMs, as defined in the JEDEC specifications.
The mechanical characteristics of the RAM expansion SO-DIMM are given in the JEDEC specification for the DDR SO-DIMM. The specification number is JEDEC JESD95. To obtain a copy of the specification, see the references listed at “RAM Expansion Modules.”
The specification defines SO-DIMMs with nominal heights of 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, and 2.0 inches. The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer can accommodate SO-DIMMS with heights of 1.25 inches or less.
The JEDEC specification defines the maximum depth or thickness of an SO-DIMM as 3.8 mm. Modules that exceed the specified thickness can cause reliability problems.
Electrical Design of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs
SO-DIMMs for the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer are required to be PC2700 compliant. For information about the PC2700 specifications, see the references at “RAM Expansion Modules.”
The electrical characteristics of the DDR RAM SO-DIMM are given in section 4.5.6 of the JEDEC Standard 21-C, release 7 (JESD-21C). To obtain a copy of the specification, see the references listed at “RAM Expansion Modules.”
The JEDEC and Intel specifications define several attributes of the DIMM, including storage capacity and configuration, connector pin assignments, and electrical loading. The specifications support SO-DIMMs with either one or two banks of memory.
Important: The memory controller on the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer uses a separate CKE signals for each bank, as called out in the JEDEC specification. SO-DIMMs that have all the CKE pins connected together do not operate properly.
The JEDEC specification for the SO-DIMM defines a Serial Presence Detect (SPD) feature that contains the attributes of the module. SO-DIMMs for use in PowerBook computers are required to have the SPD feature. Information about the required values to be stored in the presence detect EEPROM is in section 4.1.2.5 and Figure 4.5.6–C (200-pin DDR SDRAM SO–DIMM, PD INFORMATION) of the JEDEC standard 21-C specification, release 7.
Important: For a DIMM to be recognized by the startup software, the SPD feature must be programmed properly to indicate the timing modes supported by the DIMM.
Capacitance of the data lines must be kept to a minimum. Individual DRAM devices should have a pin capacitance of not more than 5 pF on each data pin.
DDR SDRAM Devices
The DDR SDRAM devices used in the RAM expansion modules must be self-refresh type devices for operation from a 2.5 V power supply. The speed of the DDR SDRAM devices must be 167 MHz or higher.
The devices are programmed to operate with a CAS latency of 2.5 or 3. At these CAS latencies, the access time from the clock transition must be +/- 0.6 ns or less for data strobes and +/- 0.7 ns for data lines. The burst length must be at least 4 and the minimum clock delay for back-to-back random column access cycles must be a latency of 1 clock cycle.
When the computer is in sleep mode, the RAM modules are in self-refresh mode and the maximum power-supply current available for each RAM module is 6 mA/128 MB (see the section “RAM SO-DIMM Electrical Limits”). Developers should specify DDR SDRAM devices with low power specifications so as to stay within that limit.
Configuration of DDR RAM SO-DIMMs
Table 4-1 shows information about the different sizes of DDR SDRAM devices used in the memory modules. The first two columns show the memory size and configuration of the SO-DIMMs. The next two columns show the number and configuration of the DDR SDRAM devices making up the memory modules.
Note: The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer does not use memory interleaving, so installing two SO-DIMMs of the same size does not result in any performance gain.
Address Multiplexing
Signals A[0] – A[12] and BA[0] – BA[1] on each RAM SO-DIMM make up a 15-bit multiplexed address bus that can support several different types of DDR SDRAM devices. Table 4-2 lists the types of devices that can be used in the PowerBook G4 17-inch computer by size, configuration, and sizes of row, column, and bank addresses.
Important: The PowerBook G4 17-inch computer supports only the types of DDR SDRAM devices specified in Table 4-2. Other types of devices should not be used with this computer.
RAM SO-DIMM Electrical Limits
Each RAM SO-DIMM must not exceed the following maximum current limits on the 2.5 V supply:
Active: 1.2 A (8 devices at 150 mA each)
Sleep: 6 mA/128 MB
Important: The restriction on sleep current is required not only to maximize the battery life but to meet the limitations of the backup battery during sleep swapping of the main battery. Developers of RAM expansion modules that exceed the limit on sleep current must include a warning to the user that battery sleep swapping may not work with those modules installed.
The Intrepid memory controller does not support 4-bit-wide SDRAM devices in any RAM expansion module.
CardBus Slot
The CardBus slot accepts one Type I or Type II card. The slot supports both 16-bit PC Cards and 32-bit CardBus Cards. The card can be removed and replaced while the computer is operating.
For information about the CardBus and the PC Card, refer to the CardBus DDK and the PC Card Manager SDK. To obtain the DDK and the SDK, see the reference at “PC Card Manager.”
© 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved. (Last updated: 2003-03-01)