PATH
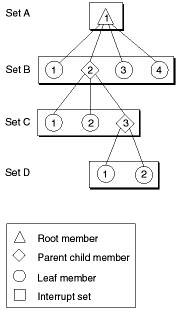
An interrupt source tree is composed of hierarchically arranged nodes. Each node represents a distinct hardware interrupt source. Nodes are called interrupt members and are arranged in interrupt sets.
An interrupt set is identified by an InterruptSetID value and is characterized as the logical grouping of all of the direct child nodes of a parent node. An InterruptSetID value has no meaning other than being unique among all InterruptSetID values. An interrupt member is identified by an InterruptMemberNumber value, which lies in the range from 1 to the number of members in the interrupt set to which the interrupt member belongs. Together, an InterruptSetID and InterruptMemberNumber group form an InterruptSetMember identifier that uniquely identifies a node in the IST.
Each interrupt set in the hierarchy represents a finer categorization of an interrupt source. The top of the tree consists of a single interrupt member that has no parent members and is referred to as the root member. The rest of the interrupt members in the tree branch down from the root member with each interrupt member acting as a child member to the interrupt members above it, and as a parent member to the interrupt members below it. When an interrupt member has no child members, it is referred to as a leaf member.
An interrupt source tree can have any number of branches, and any branch can have any number of levels. Figure 11-2 illustrates a simplified example of an interrupt source tree.
Figure 11-2 Interrupt source tree example