PATH
The Correction Data area of the gamma table contains the gamma correction data. If more than one channel's information is present, a block of information for each channel appears in red, green, blue order. There is no field of the GammaTbl structure that directly maps to the correction data; instead, correction data is appended to the gFormulaData field. To understand how correction data is organized, consider the QuickDraw representation of RGB color:
struct RGBColor
{
unsigned short red; // magnitude of red channel
unsigned short green; // magnitude of green channel
unsigned short blue; // magnitude of blue channe
};
typedef struct RGBColor RGBColor;
Effectively, the purpose of a gamma table is to map a red, green, or blue channel into another channel. This mapping serves two purposes: to move from 16 bits of significance to gDataWidth bits, and to apply luminance correction.
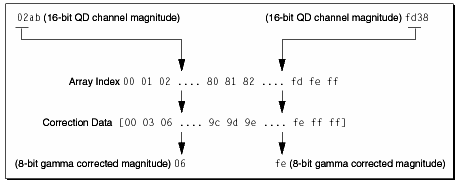
The mapping is usually accomplished by taking the most significant 8 bits of a given channel and using it as an index into that channel's correction data. Two examples of this, with gDataWidth == 8, are illustrated in Figure 13-3.
Figure 13-3 Examples of gamma table correction