QuickTime Image File Format
This appendix describes QuickTime image files, which are intended to provide the most useful container for QuickTime-compressed still images.
Most still image file formats define both how images should be stored and compressed. However, the QuickTime image file format is a container format, which describes a storage mechanism independent of compression. The QuickTime image file format uses the same atom-based structure as a QuickTime movie.
In this section:
Atom Types in QuickTime Image Files
Recommended File Type and Suffix
Atom Types in QuickTime Image Files
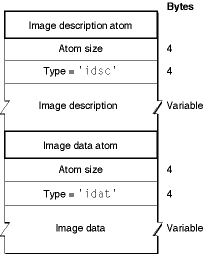
There are two mandatory atom types: 'idsc',
which contains an image description, and 'idat',
which contains the image data. This is illustrated in Figure A-1. A QuickTime image
file can also contain other atoms. For example, it can contain single-fork
preview atoms.
In QuickTime 4, there is a new optional atom type 'iicc',
which can store a ColorSync profile.
Figure A-1 shows an example QuickTime image file containing a JPEG-compressed image.
0000005E |
Atom size, 94 bytes |
69647363 |
Atom type, |
00000056 |
Image description size, 86 bytes |
6A706567 |
Compressor identifier, |
00000000 |
Reserved, set to 0 |
0000 |
Reserved, set to 0 |
0000 |
Reserved, set to 0 |
00000000 |
Major and minor version of this data, 0 if not applicable |
6170706C |
Vendor who compressed this data, |
00000000 |
Temporal quality, 0 (no temporal compression) |
00000200 |
Spatial quality, |
0140 |
Image width, 320 |
00F0 |
Image height, 240 |
00480000 |
Horizontal resolution, 72 dpi |
00480000 |
Vertical resolution, 72 dpi |
00003C57 |
Data size, 15447 bytes (use 0 if unknown) |
0001 |
Frame count, 1 |
0C 50 68 6F 74 6F 20 2D20 4A 50 45 47 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |
Compressor name, "Photo - JPEG" (32-byte Pascal string) |
0018 |
Image bit depth, 24 |
FFFF |
Color lookup table ID, -1 (none) |
00003C5F |
Atom size, 15455 bytes |
69646174 |
Atom type, |
FF D8 FF E0 00 10 4A 46 49 46 00 01 01 01 00 48 ... |
JPEG compressed data |
Important: The exact order and size of atoms is not guaranteed to match the example in Figure A-1. Applications reading QuickTime image files should always use the atom size to traverse the file and ignore atoms of unrecognized types.
Note: Like QuickTime movie files, QuickTime image files are big-endian. However, image data is typically stored in the same byte order as specified by the particular compression format.
Recommended File Type and Suffix
Because the QuickTime image file is a single-fork format,
it works well in cross-platform applications. On Mac OS systems,
QuickTime image files are identified by the file type 'qtif'.
Apple recommends using the filename extension .QIF to
identify QuickTime image files on other platforms.
© 2004, 2007 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. (Last updated: 2007-09-04)