Overview of Power Mac G5
The 64-bit desktop Power Mac G5 computer uses single and dual PowerPC G5 microprocessors and is intended for use in content creation, desktop publishing, multimedia, scientific and technical applications, and other activities that require high performance.
In this section:
Hardware Features Summary
Features of the Enclosure
System Software
Hardware Features Summary
Here is a list of the hardware features of the Power Mac G5 computer. The major features are described more fully later in this note.
Microprocessors: Three clock frequencies are available on the Power Mac G5 computer: single 1.6 GHz, single 1.8 GHz, and dual 2.0 GHz. For more information, see “PowerPC G5 Microprocessor.”
Memory caches: The PowerPC G5 microprocessors used in the Power Mac G5 computer have an internal 512 KB level 2 cache.
Processor system bus: The processor bus has 64-bit throughput (32-bit in and 32-bit out) with clock speeds of 800 MHz, 900 MHz or 1 GHz. For more information, see “Processor Bus.”
Memory bus: The main memory bus is 128 bit 333 MHz or 400 MHz. For more information, see “Main Memory Bus.”
DDR SDRAM: Eight DIMM slots for 184 pin DIMMs (dual inline memory modules) using unbuffered DDR (double data rate) SDRAM devices. A minimum of 256 MB of RAM is installed in pairs of slots, and the systems are capable of a maximum of 4 GB or 8 GB. For more information, see “Main Memory Bus.”
AGP 8x Pro card slot: The computer has an AGP 3.0 8x Pro accelerated graphics card installed in this slot. For more information, see “Accelerated Graphics Port Bus.”
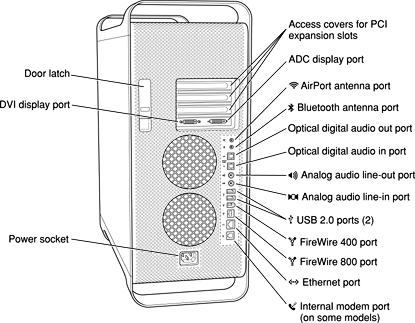
PCI expansion slots: Three PCI or PCI-X slots are provided via the HyperTransport bus. In some Power Mac G5 configurations, the slots support PCI-X: one slot supports a maximum of 133 MHz and two slots support a maximum of 100 MHz. In other Power Mac G5 configurations, the three slots support 33 MHz PCI. For more information, see “PCI or PCI-X Expansion Slots.”
Hyper Transport bus: A new high-speed bus architecture between the memory controller and device I/O. For more information, see “HyperTransport Technology.”
Graphics card: The Power Mac G5 computer comes standard with one of the following graphics cards: NVIDIA GeForce FX 5200 Ultra with 64 MB RAM or ATI Radeon 9600 Pro with 64 MB RAM. Also available as a build-to-order option is the ATI Radeon 9800 Pro with 128 MB RAM. All cards have ADC and DVI-I connectors. For more information, see “Graphics Cards.”
Power supply: The Power Mac G5 computer comes with either a 450 W or 600 W power supply.
Hard disks: An internal 7200 rpm Serial ATA hard disk occupies one of two drive bays and functions as the default boot disk. Hard disk capacities are 80 GB and 160 GB with a 250 GB build-to-order option. For more information, see “Serial ATA Interface.”
SuperDrive (DVD-R/CD-RW drive): The Power Mac G5 computer has a SuperDrive drive connected to the Ultra DMA ATA/100 bus. For more information, see “SuperDrive.”
Combo (DVD-ROM/CD-RW) drive: Instead of a SuperDrive, the Power Mac G5 computer has an optional build-to-order combination DVD-ROM/CD-RW drive connected to the Ultra DMA ATA/100 bus. For more information, see “Combo Drive.”
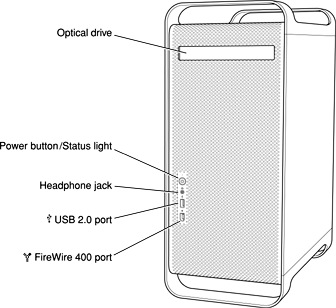
High-speed USB 2.0: The computer has three external USB 2.0 ports: two on the rear of the enclosure and one on the front. All ports support both high-speed and classic USB speeds. For more information, see “USB Ports.”
Ethernet: The computer has a built-in Ethernet port for 10Base-T/UTP, 100Base-TX, or 1000Base-TX Gigabit operation. The Ethernet port is auto-sensing and self-configuring to allow use of either a cross-over or straight-through cable. For more information, see “Ethernet Port.”
AirPort Extreme Card: Available as a build-to-order option, the 54 Mbps AirPort Extreme Card provides a wireless LAN connection. For more information, see “Wireless LAN Module.”
Bluetooth : Available as a build-to-order option, the fully-integrated Bluetooth module enables short-range wireless connections between desktop and laptop computers and a host of other peripheral devices. For more information, see “Bluetooth Technology.”
FireWire ports: The computer has two FireWire 400 ports and one FireWire 800 port. For more information, see “FireWire Controllers.”
Modem: The computer has a built-in Apple 56 Kbps modem. The modem supports K56flex and V.90 and V.92 modem standards. For more information, see “Internal Modem.”
Keyboard: The computer comes with a full-size USB Apple Keyboard. The keyboard is also a bus-powered USB hub with two USB ports. For more information, see “Keyboard.”
Mouse: The computer comes with a USB Apple Mouse, with optical tracking. For more information, see “Mouse.”
Boot ROM: The Power Mac G5 computer comes with 1 MB of boot ROM.
S/PDIF digital audio: The Power Mac G5 implements S/PDIF (Sony/Phillips Digital Interface) digital audio I/O via TOSLink optical input and digital output connectors on the rear panel. For more information, see “Sound System Overview.”
Analog audio line-in: Rear panel analog audio line-in port for self-powered microphones or other audio equipment. For more information, see “Analog Audio Line-in.”
Analog audio line-out: Rear panel analog audio line-out port for externally-powered speakers or other audio devices with line-level outputs. For more information, see “Analog Audio Line-out.”
Headphone and internal speaker: The front panel includes a headphone mini-jack and the system includes an internal speaker. For more information, see “Analog Headphone Jack.”
DVI to video adapter: The Power Mac G5 supports S-video and composite video from an optional adapter connected to the DVI port. For more information, see “DVI to Video Adapter.”
Voltage switching: Auto-ranging voltage switching accepts 100 - 240V.
Fan speed control: The speeds of the fans are thermally controlled and are automatically set as low as possible to minimize noise. System performance can be specified by a “high/reduced/automatic” pulldown option provided in the Energy Saver Control pane in System Preferences.
Energy saving: Sleep scheduling can be controlled via the Energy Saver pane in System Preferences.
Features of the Enclosure
The Power Mac G5 computer’s enclosure is a tower design. Figure 1-1 illustrates the front of the enclosure and Figure 1-2 illustrates the rear of the enclosure.
The enclosure has space for two hard disk drives and one optical device. See “Hard Disk Drives.”
To access the main logic board to install PCI or PCI-X cards or additional memory, refer to “Expansion.” For full details regarding opening and accessing the computer, refer to the Power Mac G5 Take Apart document provided by Apple Care support.
Warning: Opening the enclosure side panel impacts the thermal performance of the computer. Do not run the enclosure with the side panel open. If the air deflector inside the enclosure is removed, the fans will turn off and the system will take action to prevent over-heating.
System Software
The Power Mac G5 computer ships with Mac OS X 10.2.7 installed as the default operating system. The classic environment can be used to run Mac OS 9 applications.
To retrieve information from the I/O Registry, use the APIs in the header file IOKit/IOKitLib.h.
Computer Identification
Rather than reading the box flag or the model string and then making assumptions about the computer’s features, applications that need to find out the features of the computer should use I/O Registry calls to test for the features they require.
Asset management software that reports the kind of computer it is run on can obtain the value of the property at Devices:device-tree:compatible in the IODeviceTree plane of the I/O Registry. The model string is the first program-usable string in the array of C strings in the compatible field. For the Power Mac G5, the value of the model property is PowerMac7,2.
Power Management
A common power management strategy is implemented across all Macintosh models. The basics of Apple’s power management techniques are described in the following paragraphs.
Processor and Bus Slewing
To lower power consumption, heat generation, and fan noise, the Power Mac G5 computer incorporates an automatic power management technique called bus slewing. Bus slewing is designed to run at high processor and bus speeds and high voltage when the demand on the processor is high, and to run at low processor and bus speeds and low voltage when the demand on the processor is low. Switching between different processor/bus speeds and voltages is achieved by a gradual transition that does not impact system or application performance and operates seamlessly to the user. In slewing, the bus runs at half the speed of the processor.
The ranges of the slewed processor speeds are listed below:
Configuration | Processor range |
|---|---|
1.6 GHz | 1.3 GHz to 1.6 GHz |
1.8 GHz | 1.3 GHz to 1.8 GHz |
2.0 GHz | 1.3 GHz to 2.0 GHz |
In addition, the Power Mac G5 computer allows the user to control bus slewing mode. The options for specifying either high, reduced, or automatic processor and bus speeds are located at System Preferences>Energy Saver>Options; then select Automatic, Highest, or Reduced.
If the Power Mac G5 computer detects a system temperature that is too high, due to high ambient temperatures or other factors, it will automatically enter bus slewing mode regardless of the selected setting.
Processor States
The following processor states are defined:
Run: The system is running at maximum processing capacity with all processors running at full speed.
Idle: The system is idling; this is the default state. All clocks are running and the system can return to running code within a few nanoseconds. If the system has no work to do, it will be in idle mode.
System Modes
The Macintosh system has the following power-saving modes. If the system does not support full sleep, it will use the less efficient doze mode.
Run: The system is fully functional in normal operating mode with all components powered and operating.
Doze: The power to the disk drive motors and the display is turned off, but the power supply and fans are still on. PCI cards that don't support full system sleep (some SCSI cards, some graphics cards) will cause the machine to doze rather than fully sleep.
Full sleep: The main power supply is shut down. A trickle supply provides auxiliary power to the PCI slots and keeps the DRAM state preserved for a quick recovery. All processors are powered off with their state preserved in DRAM. All non-essential clocks in the system are suspended. This mode allows the computer to meet Energy Star sleep requirements while providing the ability to start up without rebooting. This system may be awakened by administrative network packets, keyboard or mouse activity, USB device removal, or PMU scheduled wakeup.
Off: The Power Mac G5 computer meets FEMP (Federal Energy Management Program) requirements and supports FireWire ports functioning as repeaters when operating on AC power.
Velocity Engine Acceleration
The Velocity Engine is the vector processing unit in the PowerPC G5 microprocessor. System software has been modified to take advantage of the accelerated processing that the Velocity Engine makes possible and to support low-level operations using the Velocity Engine.
For complete information on the Velocity Engine, refer to the following Apple website:
http://developer.apple.com/hardwaredrivers/ve/index.html
© 2003 Apple Computer, Inc. All Rights Reserved. (Last updated: 2003-08-20)