PATH
Figure A-3 shows what happens when the diagram in Figure A-1 is rotated clockwise.
Figure A-3 Little-endian descriptor layout
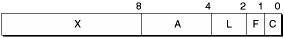
This diagram in Figure A-3 shows how a little-endian system would organize the descriptor. Notice which bytes constitute the "beginning" of each field. Instead of referring to the most significant byte of a field, the offsets refer to the least significant byte of each field. Hence, in this example, byte 4 refers to the least significant byte of the A field, while byte 7 refers to the most significant byte.
Bit numbering in a little-endian architecture naturally follows that of byte ordering; that is, bit 0 represents the least significant bit of a field. Thus, in little-endian bit field designations, the first bit shown (the most significant) has the highest bit number.