SendToSelf Apple Events
Beginning with Finder 8, all Apple events are handled in separate
threads. When the Finder receives any high-level event (including
Apple Events), it immediately suspends the event, creates a Thread
Manager task where the event will be handled, and schedules the task
for execution. Once the thread has completed execution and wishes to
return a value, Finder resumes the Apple Event.
Products patching the system and sending Apple Events to the
Finder with the send mode kSendToSelf while the Finder
is the current process may require revision. In this case,
AESend will return the error
errAEEventTimeout, which requires special handling. The
caller should handle this error by periodically attempting to extract
data from the reply event. Also, the caller should be sure to yield
time to the System so the Finder can run and process the event. When
the Finder completes processing of the event, the reply will contain
the requested data.
AppleScript Changes
The AppleScript facilities
provided by the Finder have changed. All of the scripting services
formerly provided by the Finder are still present in the operating
system; however, some of the facilities provided by the Finder have
been moved to the appropriate control panels.
Network Commands Moved to Control Panels
The Finder no longer handles creation or manipulation of network
users or groups, nor can the Finder be asked to retrieve information
about connected users or file sharing activity. These scripting
features are now handled by their respective control panels, which
can be targeted by scripts. Developers who have created scripts that
instruct the Finder to either create or modify Users or Groups or
query the Finder about file sharing details require modification for
compatibility with Mac OS 8. In most cases, such modification will
only require a change in the target application from the Finder to
either the File Sharing control panel or the Users & Groups
control panel.
|
Note:
For compatibility with the majority of scripts utilizing the
network facilities once provided by the Finder, the Finder continues
to support commands for turning on and off file sharing.
|
Revised Property Values
In order to correct an incompatibility with the 'info for'
scripting addition, the Finder has changed the values of several
properties. Specifically, the values of the properties 'folder',
'creation date', 'modification date', 'locked', and 'file type' have
changed. Compiled scripts compiled under Finder 7 will continue to
run without requiring recompilation. However, if these same scripts
are opened with the ScriptEditor under Finder 8, all former
references to these properties will have the text 'obsolete' appended
to the property name indicating the older property value. These
scripts will continue to compile and run for both Mac OS 7 and Mac OS
8; however, if the text 'obsolete' is removed, indicating the newer
property value, then the compiled script will only be run Finder 8.
|
Compatibility Note:
Scripts utilizing the new property values that have been
compiled under Finder 8 will not run with Finder 7 as the new
property values will not be recognized by Finder 7. To create a
script that will run with both Finder 7 and Finder 8, developers
should either compile and save the script with Finder 7, or they
should leave the text 'obsolete' in place when compiling with
Finder 8.
|
Application Processes
Under Finder 7, requests for 'application processes' result in a
collection of 'applications' which is actually data of type
typeProcessSerialNumber. For example, under Finder 7,
'application processes' might return {application "Script Editor",
application "Stickies"} and 'first application process' might return
'application "Script Editor "'.
Under Finder 8 the behavior of 'application processes', 'desk
accessory processes', and 'processes' has changed to always return a
list of processes. For example, the same script under Finder 8 still
returns {application "Script Editor", application "Stickies"} because
AppleScript is asking for the items as typeProcessSerialNumber.
However, in this case, 'first application process' under Finder 8,
will return 'process "Script Editor"' which is a different data type.
Developers wishing to obtain the same data type for both Finder 7 and
Finder 8 should use the query ' first application process as
«class psn »' in their scripts, which will return the value
'application "Script Editor "' with both Finders.
New Drag Flavors
Finder 8 introduces four new drag flavors --
'fdtt', 'fntb','clnm' and 'clfn' -- for
client applications who wish to support dragging to the Finder. The
appearance of any of these new flavors attached to any drag item in a
DragReference will direct the Finder to provide the
following behaviors when accepting the drag:
Limiting Valid Drop Targets to the Trash
Adding the 'fdtt' (drag to trash) flavor to any item in a
DragReference tells the Finder not to accept the drag
anywhere except to the Trash icon. No other icons of windows will
highlight. If the 'fdtt' flavor appears anywhere in a
DragReference, then it applies to all of the items in
the DragReference. The 'fdtt' flavor provides
an opportunity for applications to utilize the 'drag to trash' model
for, say, allowing users to delete selections by dragging them to the
trash. 'fdtt' flavors do not contain any data.
Disabling Finder Tracking Behavior
Adding the 'fntb' (no tracking behavior) flavor to any item in a
DragReference instructs the Finder to ignore the drag
entirely. Neither windows or icons will highlight to accept drags, nor will any
spring-opening occur in the Finder when the 'fntb' flavor is included in
a DragReference. If the 'fntb' flavor appears
anywhere in a DragReference, then it applies to all of
the items in the DragReference. 'fntb' flavors
do not contain any data.
Controlling Clipping File Names
The 'clnm' and 'clfn' flavors have been added to
provide applications with better control over the naming of clipping
files. These flavors are used by the Finder in the following steps
that it uses to determine the name for a clipping file:
- If the item contains a
'clnm' flavor
(flavorTypeClippingName), then this value (a pascal
string) is used in the template "^0 clipping" to name the file.
This is the preferred method for new applications. Usually, the
application should provide the name of the document from which the
clipping was dragged.
- If the file name was not assigned in the above and the item
contains a
'clfn' flavor, then this value (a pascal
string) is used as the complete file name.
- If the clipping file name was not established by either of the
above methods, then the flavors are examined in order until a
'TEXT', 'PICT', or 'snd ' flavor is
found. If one of these flavors is found, then the clipping file is
named either "text clipping", "picture clipping", or "sound
clipping" respectively.
- as a last resort, the name "untitled clipping" is used.
- If the name assigned by the above steps is already in use,
then a number is appended to the name (or appended and incremented
until a unique name is established). Also, if the resulting name
is longer than 31 characters, the name is truncated in the middle
and an ellipsis is added. For example, "A Very Long Doc...
clipping 100".
|
Note:
Developers utilizing the 'fdtt', 'fntb',
'clnm', and 'clfn' flavors are not required
to create additional drag items to attach them to when
including them in a DragReference. To request the
behaviors defined for each of these flavors from the Finder,
simply attach them to any drag item included in the DragRef; and,
as these special flavors define behaviors and contain no data,
when adding any of these flavors to a DragReference
the flavorNotSaved flag must be set in the FlavorFlags
parameter in calls to AddDragItemFlavor. The Finder will
provide the behaviors defined for each of the new flavors if
they appear anywhere in the DragReference.
|
Other Important Finder 8 Facts
- Some of the formerly 'reserved for future use' flags in the
FXInfo structure used for directories and volumes are now used for
specific purposes. Archive developers should take care to preserve
all these flags for folders when including them in archives.
- Memory usage for applications reported in the "About This
Computer..." window now displays the sum of both the application's
memory partition size and the total size of any temporary memory
allocated by the application.
- Finder 8 performs all drawing operations to off-screen GWorlds
before displaying information on the screen via
CopyBits. To streamline memory requirements, the
Finder limits the depth of the off-screen drawing buffers it uses
to 8-bits; hence, when a 16-bit or 24-bit monitor is being used
CopyBits performs a translation between the two bit
depths (blitting). Video driver (accelerator) authors for such
displays should be aware of this fact and should ensure that blits
of this variety are accelerated, as probably the most common
blitting operation in Mac OS 8 will be from an 8-bit-deep
off-screen GWorld to the monitor.
- The new Finder opens stationery documents in
non-stationery-aware applications by automatically creating a copy
of the stationery document and then passing the copy along to the
appropriate application via an "open documents" ('odoc') Apple
Event . Stationery-aware applications interact with Finder 8 in
the same way as they did under Mac OS 7.x.
- New invisible files created by the Finder include
"OpenFolderListDF" and "DesktopPrinterDB".
- Many of the undocumented internal structures maintained by the
Finder have changed with this release. Programs making assumptions
regarding the organization or content of these internal structures
will not be compatible with Finder 8.
- Finder 8 does not support QuickDraw GX desktop printing.
(QuickDraw GX printing is no longer
supported under my Mac OS 8.)
- Finder 8 does not support desktop ("Get Info...") comments for
floppy disk volumes.
- When the Finder communicates with an old style
'cdev' type control panel, it turns off the new
Appearance facilities. As a result, old
style 'cdev' type control panels and the controls
they contain appear as they would in System 7.
- Previous versions of the Finder would only search for custom
help balloons in the resource forks of applications, control
panels, and system extensions. The new Finder searches for custom
help balloons in the resource fork of any file. Developers wanting
to override the standard help balloons displayed for other files
should include a standard
'hfdr' ID -5696 resource
describing the file in the file's resource fork.
Related Materials:

|
Inside the System file
|
The system file contains routines and resources
responsible for running the computer. This section describes new
features and corrections built into the System file. These items are
always present under Mac OS 8, even when shift key is held down at
system startup.
Native CPU Family Gestalt
A new Gestalt selector
gestaltNativeCPUfamily ('cpuf') has been
added that will always return the CPU family of the current PowerPC
processor. The new gestaltNativeCPUfamily selector
returns the same values as the gestaltNativeCPUtype
('cput'), but it does not distinguish between variants
within the same processor family. For example, the following table
illustrates the difference between the new
gestaltNativeCPUfamily selector and the older
gestaltNativeCPUtype selector:
|
PowerPC Processor
|
gestaltNativeCPUfamily
in Mac OS 8
|
gestaltNativeCPUtype
since System 7.5
|
|
601
|
gestaltCPU601
|
gestaltCPU601
|
|
603
|
gestaltCPU603
|
gestaltCPU603
|
|
603e
|
gestaltCPU603
|
gestaltCPU603e
|
|
603ev
|
gestaltCPU603
|
gestaltCPU603ev
|
|
604
|
gestaltCPU604
|
gestaltCPU604
|
|
604e
|
gestaltCPU604
|
gestaltCPU604e
|
This new selector allows developers to test for the presence of
particular family-specific PowerPC processor features without having
to know all of the members of a CPU family.
Alias Manager
The Alias Manager is the part of the operating system
that communicates with the file system to maintain alias records that
are used to keep track of file and folder locations. The Alias
Manager does not create Finder alias files; the Finder creates these
files and stores alias records created by the Alias Manager in them.
MatchAlias wasn't checking for off-line volumes when
kARMNoUI was specified among its flag parameters. This
could have lead to some superfluous alerts requesting the off-line
disks when the Alias Manager attempted to access the volume
information. The Alias Manager now disables the File Manager's "disk
switch alert" when the kARMNoUI rule is specified.
Related Materials:
- The
Alias
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: Files.
- The
Alias
Manager section on page 2-64 of Inside Macintosh:
QuickTime.
- Technote FL30, "Resolving Alias
Files Quietly"
ATA Manager 4.0
ATA stands for AT-Attachment, and is a bus protocol
used by the Mac OS for communications with IDE devices such as Hard
Disks, CD ROMs, and other IDE devices in some Mac OS compatible
computer models. Machines with installed IDE hard drives or ATAPI CD
ROM drives use the ATA Manager (this includes most Performas and
PowerBooks).
The routine ATA_RegAccess function has been updated to work
correctly on PowerBook 3400 machines.
Code Fragment Manager 68K (CFM-68K) 4.0
The 68K Code Fragment Manager (CFM-68K) is the 68K
implementation of the Code Fragment Manager. The 68K Code Fragment
Manager is the part of the Mac OS on 68K machines that loads 680x0
code fragments into memory and prepares them for execution. CFM-68K
is not appropriate for use on PowerPC machines.
- In Mac OS 8, CFM-68K has been included in the system file.
- The following CFM-68K shared libraries are now stored in the
data fork of the system file:
- InterfaceLib
- StdCLib
- AppleGuideGlueLib.68k
- DragLib
- QuickTimeLib
- ThreadsLib
- ObjectSupportLib
- AppleScriptLib
- Translation
- CollectionsLib
- FoldersLib
Related Materials:
- Technote TN1084, "Running CFM-68K
Code at Interrupt Time: Is Your Code at Risk?"
- Technote TN1077, "Calling CFM
Code From Classic 68K Code, or There and Back Again, A Mixed
Mode Magic Adventure"
- The CFM-68K SDK.
Collection Manager 1.1
The Collection Manager provides a data storage and
retrieval service usable from applications for the purposes of
maintaining small collections of variable sized data elements. This
facility has been moved from QuickDraw GX
to the Toolbox and is now included in the System file. The Mac OS 8.0
version of the Collection Manager contains the following corrections:
- Flattening a collection containing items with data of length
zero produced a incorrectly formed flattened data stream. A
collection unflattened from this buffer would also be incorrect;
the zero-length items would be thought to have length 0xFFFFFFF8
instead of zero.
- When replacing the data of an existing collection item, if
there was not enough memory to add the new data, the collection
was corrupted by the error-handling code. After control returned
to the caller, the data size of the item being replaced was
thought to be four bytes larger than it actually was.
- When
AddCollectionItem or
ReplaceIndexedCollectionItem replaced an existing
item with new data that was larger than the item's old data, a
pointer to an unlocked handle was cached across a heap operation.
|
Compatibility Note:
Developers requiring the Collection Manager must link with
CollectionsLib under Mac OS 8 as it will not be accessible via
the QuickDraw GX library. The Mac OS 8.0 version of
CollectionsLib includes glue for both CFM-68K and PowerPC CFM
callers. In Mac OS 8, the
gestaltCollectionMgrVersion selector returns
version 1.1 (0x01108000).
|
Related Materials:
Communications Toolbox
The Communications Toolbox provides an API for basic
communications and connection services.
A problem in the StandardNBP routine where it was
possible for a list structure exceeding 32k to be allocated when a
large number of names were requested has been corrected.
Related Materials:
- Apple Computer, Inc. Inside the Macintosh Communications
Toolbox. Addison Wesley.
Control Manager
The Control Manager provides facilities for drawing
and processing user interaction with controls drawn on the screen.
The new Appearance Manager extends the functionality of the
Control Manager. See the Appearance Manager documentation and SDK for
further information.
Related Materials:
Desktop Manager
The Desktop Manager provides routines for accessing
desktop database files on Mac OS volumes.
- The Desktop Manager can now support volumes managed by File
System Manager agents. See the File
System Manager section for more information.
- For asynchronous Desktop Manager requests, 68K register
D0 is now saved and restored around completion
routines.
PBDTGetInfo now works correctly. Previously,
PBDTGetInfo usually returned nsvErr (no
such volume).PBDTOpenInform and PBDTGetPath no
longer crash if called before the Process Manager is available.
Now, they now return paramErr and do nothing if
called before the Process Manager is available.- All former Desktop Manager patches were integrated into the
main code, reducing the number of patches in the system as a
whole.
Related Materials:
Device Manager
The Device Manager provides a standard programming
interface for communications between applications and code that is
designed to communicate with particular hardware devices (although
some "device drivers" do not actually drive devices).
- The PCI
DriverLoaderLib now correctly expands the unit table
as necessary when loading new drivers.
Related Materials:
- The
Device
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: Devices.
- Designing PCI Cards & Drivers
Dialog Manager
The Dialog Manager provides automated user interface
facilities for managing user interactions with dialog windows.
- Previously,
AppendDITL and
ShortenDITL did not correctly resize the
AuxWinRec, and random memory was being used to draw
the new items. This has been corrected.
ShortenDITL was calling
ReleaseResource on 'PICT' and
'ICON' items. It no longer does this.ShortenDITL and AppendDITL have been
enhanced to support 'cicn' items in non-color
dialogs.- The new Appearance Manager extends the functionality of the
Dialog Manager. See the Appearance Manager documentation and SDK
for further information.
- When Appearance is turned on, the Dialog Manager ignores all
entries in custom dialog color tables (type 'dctb') resources
except for the content color entry.
|
Compatibility Note:
Developers drawing an outline around the default button in
dialog windows using the older black and white
FrameRoundRect method should modify their code for
compatibility with the new Appearance facilities. To display a
dark outline around the default button in a dialog box, call
the routine SetDialogDefaultItem to ensure that
the dark outline drawn around the default button has the proper
appearance.
|
Related Materials:
Disk Initialization Package
The Disk Initialization Package provides formatting
services for disks.
The Disk Initialization Package now has platinum Appearance.
Related Materials:
FKEYs
FKEYS are executable code resources, stored in the
system file, that are invoked by typing a command-shift-number
combination, where the number is equal to the resource ID of the FKEY
resource.
Under Mac OS 7.6 and Mac OS 7.6.1 the FKEY 3 & FKEY 4 routines
would fail to capture the screen if At Ease was installed but
inactive. This problem has been corrected.
Related Materials:
File Manager
The File Manager provides services for storage and
retrieval of disk based information.
- A race condition could occur in the File Manager when it was
calling synchronous-only device drivers. This problem has been
corrected.
- The File Manager's disk cache I/O code now breaks large
requests into smaller requests that can be held in memory when
Virtual Memory is turned on. This ensures that large File Manager
_Read or _Write I/O operations no longer fail with a
notEnoughMemory error if the I/O buffer is larger
than what can be held by Virtual Memory.
- The user is now notified when a write-behind operation from
the disk cache fails as a result of an error returned by the disk
volume's device driver. The notification message on U.S. systems
will read:
There is a problem with the disk VolumeName. Some information
may have been lost.
Check any recently-used files for data loss, and use a disk
repair program on the disk.
- If Virtual Memory is on, the disk cache size may be reduced to
a size that can be held by Virtual Memory.
- Internal changes were made to the disk cache to support
new File System Manager calls.
Related Materials:
- The
File
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: Files.
- Technote FL16, "File Manager
Performance and Caching"
File System Manager
The File System Manager manages the use of foreign
file systems. The File System Manager provides a general means by
which foreign file systems can be installed, identified, and
interfaced to the Operating System.
- Added new File System Manager API calls,
UTVolCacheReadIP and UTVolCacheWriteIP.
These two calls work much like UTCacheReadIP and
UTCacheWriteIP except that they read or write volume
blocks instead of file blocks.
UTBlockInFQHashP no longer does anything and
always returns noErr.- File System Manager volumes can now utilize
Desktop Manager support from the Mac
OS Desktop Manager code (the same Desktop Manager code used on HFS
volumes). For an FSM-based foreign file system to get Mac OS
Desktop Manager support for its volumes, it needs to do two
things:
- Set the
hfsCIWantsDTSupportBit (bit 17) in its
HFS component compInterfMask field. This tells the
Desktop Manager that volumes with that foreign file system's
File System ID should be supported by the Mac OS Desktop
Manager instead of being passed on to the foreign file system's
HFSCIProc.
- When the foreign file system responds to
PBHGetVolParms requests, it needs to set the
bHasDesktopMgr and bHasBTreeMgr bits
in the vMAttrib field of the
GetVolParmsInfoBuffer. Important: The Mac OS
Desktop Manager only supports volumes which are at least two
megabytes (0x00200000 bytes) large. If your foreign file system
supports volumes smaller than two megabytes, then you should
not set the bHasDesktopMgr and
bHasBTreeMgr bits on those small volumes.
- The File System Manager's
_Control
csCode #22 patch no longer affects non-disk drivers.
|
Warning:
The UTVolCacheWriteIP routine should not be
used under Mac OS 8.0 because it triggers a crashing bug.
This bug will be fixed in the next update to FSM.
|
Related Materials:
Folder Manager
The Folder Manager provides facilities for locating
"special" folders like the Extensions folder in the System Folder
without relying on the names of those folders. This aids application
localization.
Developers can now register their own special folders that can be
accessed using the FindFolder routine. Also, facilities
have been added so developers can direct future versions of the
Finder to auto-route certain file types into directories they
register with the Folder Manager. Interested developers should refer
to the Folder Manager Technote for more
information.
The Folder Manager now correctly gives ownership and blank
(inherited) access privileges to folders it creates on remote server
volumes.
The following folders are registered in Mac OS 8:
|
Folder Name
|
Type
|
Location
|
New?
|
Contents
|
|
System Folder
|
'macs'
|
it is the blessed folder |
|
System files and folders
|
|
Desktop Folder |
'desk'
|
in the root directory
|
|
The Desktop
|
|
Trash
|
'trsh'
|
in the root directory
|
|
The Trash
|
|
Network Trash Folder
|
'empt'
|
in the root directory
|
|
The Trash on network volumes
|
|
PrintMonitor Documents
|
'prnt'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
PrintMonitor documents
|
|
Startup Items
|
'strt'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
items opened at startup
|
|
Apple Menu Items
|
'amnu'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
items in the Apple Menu
|
|
Control Panels
|
'ctrl'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
control panels
|
|
Extensions
|
'extn'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
system extensions
|
|
Fonts
|
'font'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
Fonts and Font Suitcases
|
|
Preferences
|
'pref'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
Preferences files
|
|
Temporary Items
|
'temp'
|
in the root directory
|
|
Temporary files
|
|
Shutdown Items
|
'shdf'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
|
Items opened at shutdown
|
|
Cleanup at Startup
|
'flnt'
|
in the root directory
|
yes
|
items deleted at startup
|
|
Application Support
|
'asup'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Application-specific files
|
|
Extensions (Disabled)
|
'extD'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Disabled System Extensions
|
|
Control Panels (Disabled)
|
'ctrD'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Disabled control panels
|
|
System Extensions (Disabled)
|
'macD'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Disabled System Extensions
|
|
Startup Items (Disabled)
|
'strD'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Disabled Startup Items
|
|
Shutdown Items (Disabled)
|
'shdD'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Disabled Shutdown Items
|
|
Applications
|
'apps'
|
in the root directory
|
yes
|
Application programs
|
|
Printer Descriptions *
|
'ppdf'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Printer description files
|
|
Editors
|
'oded'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
OpenDoc Editors
|
|
Text Encodings
|
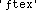
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Text encoding extensions
|
|
Stationery
|
'odst'
|
in the root directory
|
yes
|
OpenDoc Stationery
|
|
Internet Plug-Ins
|

|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Internet related plug-in files
|
|
Control Strip Modules
|
'sdev'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Control Strip Modules
|
|
Assistants
|
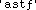
|
in the root directory
|
yes
|
Configuration assistants
|
|
Utilities
|
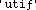
|
in the root directory
|
yes
|
Assorted utilities
|
|
Contextual Menu Items
|
'cmnu'
|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Contextual Menus
Plug-ins
|
|
Scripting Additions
|

|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
AppleScript Extensions
|
|
Printer Drivers
|

|
in 'System Folder'
|
yes
|
Printer Drivers
(not used by the system)
|
|
Note:
* The LaserWriter driver (versions 8.5.1 and before) does
not take advantage of the 'ppdf' FindFolder feature and still only looks
in the Extensions:Printer Descriptions folder for PPDs. This will be
fixed in a future release of the LaserWriter 8 driver. |
Finder 8 only creates a subset of the folders listed above
(namely: "Apple Menu Items", "Control Panels", "Extensions",
"Fonts", "Preferences", "Shutdown Items", and "Startup Items").
Other folders are created as they are needed.
Special new folders for developers:
The Application Support Folder. The new "Application
Support" folder (type 'asup') is located in the System
Folder. This folder is designated as the location where
applications should place their private extensions and plug-in
files. Applications and third-party extensions can install any
files or folders required by their software in this folder.
Apple does not define the contents of this folder.
The Internet Plug-Ins Folder. The new "Internet
Plug-Ins" folder (type  ) in the System Folder is designated as a
common location for the storage of plug-ins for applications
such as web browsers. ) in the System Folder is designated as a
common location for the storage of plug-ins for applications
such as web browsers.
Cleanup at Startup. The new "Cleanup at Startup" folder
provides an alternative location for developers to store their
temporary files. Leftover items located in the traditional
temporary files folder (type 'temp' )
are moved to the trash at system startup which may not always be
desirable and can be a nuisance to users. Most often, this situation
will occur if a application creates several temporary files is aborted
and has no chance to delete them. To avoid this condition developers can
place their temporary files in the "Cleanup at Startup" folder (type 'flnt' )
who's contents are automatically deleted at system startup. Developers
should not depend on this facility for deleting their temporary files;
rather, it should be used to ensure unusable temporary files will not
appear in the trash after system startup.
Related Materials:
Font Manager
The Font Manager provides system wide services for the
retrieval of symbols and glyphs for display of textual information.
|
Compatibility Note:
The default system font has changed and the system font can
be selected by the user. The original system font, Chicago, is
still present in the system file; however Mac OS 8 installs
with Charcoal as the system font. Developers shouldn't make any
assumptions regarding the system font in their applications.
Namely, don't assume that the system font contains a bitmap
character set for a particular font size.
|
Related Materials:
Help Manager
The Help Manager is responsible for the drawing and
display of Help Balloons and the Help menu.
- The Help Menu has been moved from the question mark icon
located on the rightmost side of the menu bar to a menu entitled
"Help" that appears to the right of the application's menus.
- A new routine,
HMShowOneBalloon, has been added
to the Help Manager. It is utilized by the
Contextual Menu Manager.
- A problem where balloons were flickering before being
displayed correctly while menu selections were being tracked from
hierarchical menus to the previous or next menu item in the parent
menu has been corrected.
|
Compatibility Note:
To avoid displaying two menus entitled "Help" in the menu
bar, developers should move any menu commands from their own
help menus into the Help Manager's help menu.
|
Related Materials:
List Manager
The List Manager is the part of the operating system
providing standard user interface facilities for drawing and managing
user interaction with lists of items.
Under some circumstances, calls to LSize could
mistakenly validate a part of the window containing the list outside
of the list's boundary rectangle, resulting in incorrect drawing
during the update event that following the call to
LSize. This problem has been corrected.
Related Materials:
- The
List
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: More Macintosh
Toolbox.
Memory Manager
The Memory Manager is the part of the operating system
responsible for managing memory allocation requests.
- The routine
PurgeMem was not returning
memFullErr when it could not allocate enough space.
PurgeMem has been corrected to report errors
correctly.
Related Materials:
Menu Manager
The Menu Manager is the part of the operating system
responsible for both drawing the menu bar and drawing menus and pop-up
menus on the screen while the mouse is being held down.
- The execution speed of
AppendResMenu has been
improved. Previously, this call was performing an insertion sort on
the menu handle itself when adding resource names to a menu. This
method was found to be slow when large menus were being created. Now,
the resource names are pre-sorted before they are added to the menu.
- Since System 7.5,
MDEF 0 was leaking memory when
displaying pop-up menus.
- There have been extensions the Menu Manager's API to
support Contextual Menus. For further details, see the
Contextual Menu Manager section.
- On some machines, including the 8100/110, Centris 650, and
840AV, clicks on dynamically allocated pop-up menus displayed by
applications or by the pop-up menu CDEF were leaking handles into
both the system heap and the Process Manager heap . This space
would eventually be recovered when the application quit, however
it would remain in memory until then. This problem has been
present on some machines since System 7.5 and has been corrected
in Mac OS 8.
- CountMItems used to fail for menus containing items with more
than 251 characters. This problem has been corrected.
- When Appearance is turned on, the Menu Manager now ignores all
entries in custom menu color table ('mctb') resources except for
the text color entry. If a default menu bar color is defined, then
no theme colors will be used and the default color specified in
the 'mctb' is used for all of the application's menus.
- The Menu Manager's API has been extended by the new Appearance
Manager. See the Appearance Manager documentation and SDK for
further information.
|
Compatibility Note:
Developers displaying pop-up menus in applications should
use the popup control rather than calling the menu manager
directly to ensure their pop-up menus are displayed correctly
when system-wide appearance is enabled.
|
Related Materials:
ObjectSupportLib 1.2
ObjectSupportLib provides routines for
AppleScript extensions and applications
providing AppleScript services.
- The ObjectSupportLib has been moved to the data fork of the
system file to prevent other older versions in the extensions
folder from being used (older versions in the Extensions folder
will not be loaded).
- This is a fat version of the Object Support Library for both
PowerPC and 68K.
Related Materials:
- Technote TN1095, "Object Support
Library Version History"
Process Manager
The Process Manager shares the processor among
multiple applications. Mac OS 8 includes the following new features
in the Process Manager:
- To avoid running out of temporary memory when applications are
launched, the Process Manager attempts to reserve 300K of heap
space for temporary memory allocations. For example, if there is
900k available for applications and an application is launched
whose preferred size is set to 10MB (and its minimum size is
200K), then it will be launched in a 600K partition leaving 300K
free for temporary memory allocations. However, launches that were
permitted before are still allowed. For example, if there is only
400k free and the same application is launched, then it will be
launched in a 200k partition leaving 200k free for temporary
memory allocations.
- A problem with memory calculations done by the Process Manager
on systems with 256 megabytes of memory installed has been
corrected.
- Active Time Manager tasks incorrectly left behind by an
application are now removed by
ExitToShell if the
TMTask record or the tmAddr field in the
TMTask record are in the application's heap.
- With Mac OS 8 the Process Manager defines a new flag developers
can use to control the hiding of processes as they are switched
out. And, the new HideOnSwitch flag can be accessed using the routines
GetHideOnSwitch and SetHideOnSwitch. When
the HideOnSwitch flag is set to true, processes are hidden whenever
they are switched from the foreground process to a background process.
HideOnSwitch is a global flag that applies to all running processes
during process switching.
Bit sixteen (gestaltHideLayerOnSwitchSupport) of the response
returned by the gestaltOSAttr Gestalt selector can be used to
determine if the HideOnSwitch flag is available and it's accessor
routines are defined. If this bit is set to one then the
following routines are available and can be called.
enum {
gestaltHideLayerOnSwitchSupport = 16
};
extern pascal void SetHideOnSwitch(Boolean setValue)
THREEWORDINLINE(0x3F3C, 0x006B, 0xA88F);
extern pascal Boolean GetHideOnSwitch(void)
THREEWORDINLINE(0x3F3C, 0x006C, 0xA88F);
Where SetHideOnSwitch sets the value of the HideOnSwitch flag,
and GetHideOnSwitch retrieves the value of the HideOnSwitch flag.
As there are no entry points for these routines in InterfaceLib,
CFM callers cannot link with them directly. To call these routines
from CFM applications, developers should compile and link with
the following code:
#if GENERATINGCFM
pascal void SetHideOnSwitch(Boolean setValue) {
enum {
uppSetHideOnSwitchProcInfo = kStackDispatchedPascalStackBased
| DISPATCHED_STACK_ROUTINE_SELECTOR_SIZE(SIZE_CODE(sizeof(unsigned short)))
| DISPATCHED_STACK_ROUTINE_PARAMETER(1, SIZE_CODE(sizeof(unsigned char)))
};
CallUniversalProc(GetToolTrapAddress(_OSDispatch),
uppSetHideOnSwitchProcInfo, 0x006BL, setValue);
}
pascal Boolean GetHideOnSwitch(void) {
enum {
uppGetHideOnSwitchProcInfo = kStackDispatchedPascalStackBased
| RESULT_SIZE(SIZE_CODE(sizeof(unsigned char)))
| DISPATCHED_STACK_ROUTINE_SELECTOR_SIZE(SIZE_CODE(sizeof(unsigned short)))
};
return (Boolean) CallUniversalProc(GetToolTrapAddress(_OSDispatch),
uppGetHideOnSwitchProcInfo, 0x006CL);
}
#endif
Related Materials:
- The
Process
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: Processes.
- Technote TN1070, "Background-Only
Applications"
- Technote PS510, "Process
Manager Q&As"
Script Manager 8.0
The Script Manager provides facilities for display and
retrieval of number, date, time, and other information in a
language-independent way.
PowerPC implementations of the routines
CharacterByteType, CharacterType,
TransliterateText, and FillParseTable have
been added.
Related Materials:
SCSI Manager
The SCSI Manager is the part of the operating system
responsible for communications with connected SCSI devices.
A problem where large volumes (larger than four gigabytes) were
not being mounted correctly at startup has been corrected. Some of
the disks on which these volumes reside were taking too long to spin
up during the first scan of the SCSI bus and were not being
recognized by the system. The system now scans the bus again later in
the boot cycle looking for volumes that missed the first scan.
Related Materials:
Serial Driver
The Serial Driver provides serial communications
services for either the printer port or the modem port using the
Device Manager API. The Mac OS 8 Serial Driver includes the following
changes:
- The Serial Driver was leaving DCD interrupts enabled after it
was closed. The Serial Driver now correctly disables DCD
interrupts when it is closed.
- Extensions which called
OpenDriver to open the
serial ports during startup would crash the machine. In this case,
the OT/PPP Serial Arbitrator was calling
GetCurrentProcess before the trap was installed in
the system. This problem has been corrected.
Related Materials:
- The
Serial
Driver chapter of Inside Macintosh: Devices.
- Technote TN1018, "Understanding
the SerialDMA Driver"
Sound Manager
The Sound Manager provides facilities for playback and
recording of digitized sounds.
Calls to SPBSetDeviceInfo with
siPlayThruOnOff to turn playthrough off while speech
recognition is turned on was incorrectly causing all sound to be
suppressed on 5200, 5300, 6200, and 6300 machines. This problem has
been corrected.
Related Materials:
- The
Sound
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: Sound.
- Technote TN1048, "Some Sound Advice:
Getting the Most Out of the Sound Manager"
StdCLib 3.4.4
StdCLib is a shared library located in the ROM on all
PowerPC-based Mac OS compatible computers providing functionality for
programs compiled using the C language. StdCLib has been present on
all PowerPC models, and prior to System 7.6 updates were provided via
the StdCLibInit system extension. Mac OS 8 includes a new version of
the StdCLib in the System file's data fork containing the following
corrections:
printf "e" format has been modified to display
full precision for 128-bit long double values,- a full rewrite of memory allocation subsystem:
malloc, calloc, realloc,
free
- text files created by tools have their creator set to
'MPS ' not 'ttxt',
- Device handlers are initialized to
NULL in
addDevHandler; this prevents a possible crash if the
user installs a device handler.
Related Materials:
- The StdCLib section in
Technote TN1090, "Mac OS 7.6"
- The StdCLib release notes on ETO #23.
Virtual Memory Manager
The Virtual Memory manager provides virtual memory
services for the Mac OS. The following changes have been made in the
Virtual Memory Manager:
- Virtual Memory was made both smaller and faster by removing
24-bit code and other dead code, using a better compiler, and
optimizing source code. These changes mostly affect Virtual
Memory's performance in:
- handling page faults
- patches to other parts of the Mac OS
- Virtual Memory's APIs (DeferUserFn, HoldMemory, LockMemory, etc.)
- handling of deferred user code
- Virtual Memory's page reuse algorithm was improved.
- Virtual Memory's loader code is more robust.
- Virtual Memory's patch on
SCSIGet now holds 2K of
the user stack while the SCSI transaction is in progress so it
cannot be accidentally paged out.
- The two primary causes of System Error 112
(
dsVMDeferredFuncTableFull) have been removed.
Virtual Memory's deferred user function table was made larger, and
calling InxTime more times than RmvTime
no longer uses additional entries in the deferred user function
table.
- A race condition was fixed in Virtual Memory's Time Manager
patches. Before, if a
RmvTime request was made from
code that interrupted either PrimeTime of the same
task or the execution of the same task, a system crash could
occur.
- Deferred system operations (Time Manager tasks, I/O completion
routines, etc.) are always run in processor supervisor mode.
Before, if a deferred system operation was deferred while running
in processor user mode, Virtual Memory unexpectedly switched to
the user stack when it tried to run the deferred operation, and
this crashed the system.
Related Materials:
Window Manager
The Window Manager is part of the Mac OS providing
facilities for drawing and maintaining windows on the screen.
When Appearance is turned on, the Window Manager now ignores all
entries in custom window color table ('wctb') resources except for
the content color entry.
|
Compatibility Note:
Developers should not make any assumptions regarding the
shape or size of a window's structure region. Also, your
application should not assume that the content region of a
window has no border. To determine the shape and size of a
window's border, calculate the difference between the content
region and the structure region. For example, to calculate the
height of the title bar for a window, following routine could
be used:
|
/* TitleBarHeight -- height of the window's topmost border */
OSErr TitleBarHeight(WindowPtr theWindow, short *height) {
RgnHandle structure, content;
structure = content = NULL;
if ((structure = NewRgn()) == NULL) goto bail;
if ((content = NewRgn()) == NULL) goto bail;
GetWindowStructureRgn(theWindow, structure);
GetWindowContentRgn(theWindow, content);
*height = (**content).rgnBBox.top - (**structure).rgnBBox.top;
DisposeRgn(structure);
DisposeRgn(content);
return noErr;
bail:
if (structure != NULL) DisposeRgn(structure);
if (content != NULL) DisposeRgn(content);
return memFullErr;
}
Related Materials:
WorldScript Power Adaptor 7.5.3
The Worldscript Power Adaptor provides language
specific text services for the Mac OS.
The Worldscript Power Adaptor has been moved to the System file.
It is no longer provided as a separate extension. If the extension is
found in the extensions folder it will be moved to the "Extensions
(disabled)" folder at system startup time.
Related Materials:
- The
WorldScript
I section in "Appendix A - Built-in Script Support" of
Inside Macintosh: Text.
- The
WorldScript
II section in "Appendix A - Built-in Script Support" of
Inside Macintosh: Text.

|
Apple Menu Items
|
Items in the Apple Menu Items folder appear in the
Apple Menu. Files of type 'APPD' are auto-routed to the Apple Menu
Items folder when they are dropped into the System Folder's icon.

|
Apple System Profiler 1.2
|
The Apple System Profiler provides a simple way to
obtain information regarding the current system configuration.
Information provided by the Profiler is useful for customer support
representatives in assisting users.
- Some additional information is now displayed.
- Names of newer machines are displayed.
- The user interface has been changed and reorganized.

|
Connect To... 1.0
|
Connect To... is a new small
AppleScript applet allowing for quick
access to an internet URL. URLs are dispatched through the Internet
Config extension.

|
Stickies 1.0.3
|
A new version of the Stickies utility featuring a few
cosmetic and implementation improvements.

|
SimpleSound 1.0
|
A new addition to the Apple Menu Items folder,
SimpleSound allows for simple convenient access to sounds installed
in the System file.

|
Control Panels
|
Control Panels provide user interface facilities for
custom configuration of the system. Files of type 'APPC'
are auto-routed to the Control Panels folder when they are dropped
onto the System Folder's icon. Also, starting with Mac OS 7.6, files
of type 'APPC' may contain 'INIT' resources
that will be executed at system startup time.
Control panels may contain system extensions. For such a system
extension to be active, the control panel must be located in the
Control Panels folder when the system starts up. Extensions within
control panels are not loaded if the shift key is held down while the
system is starting up.
In Mac OS 8, many of the standard control panels have been revised
to support the new Apple platinum
Appearance, and some of the file types and
creator codes for control panels have been changed.

|
Appearance 1.0
|
The Appearance control panel provides user interface
configuration facilities for the appearance of graphical user
interface elements throughout the system. It replaces both the older
Color and WindowShade control panels and provides a super-set of the
features that were provided by these items.
Related Materials:

|
Apple Menu Options 1.1.3
|
The Apple Menu Options control panel provides user
interface configuration facilities for the appearance and behavior of
the Apple Menu. There are some corrections present in this
implementation of the Apple Menu Options control panel.
- A problem where under certain conditions Apple Menu Options
would stop tracking Recent Servers has been corrected.
- Apple Menu Options no longer creates the 'recently used'
folders if those options are turned off.

|
AutoRemounter 1.2.5
|
The AutoRemounter control panel provides facilities
for re-mounting network volumes on portable Mac OS compatible
computers after waking the machine from sleep state.
This version has been updated to support changes in
AppleShare authentication techniques.

|
Desktop Pictures 1.0
|
Desktop Pictures replaces the Desktop Patterns control
panel. Desktop Pictures allows the user to configure the desktop to
be drawn using an image stored in a picture file. Unlike the older
Desktop Patterns control panel, Desktop Pictures uses stand-alone
image files to retrieve image data rather than resources.
- Desktop Pictures is an
'APPC'and will be
auto-routed to the Control Panels folder when it is dropped onto
the System Folder icon.
- Desktop Pictures supports a suite of
AppleScript commands for configuring
the desktop pattern.
- Third-party extensions and applications can query the current
status of Desktop Pictures by using the following
Gestalt selector:
enum {
/* the 'dkpx' selector is installed by the Desktop Pictures INIT */
gestaltDesktopPicturesAttr = 'dkpx',
/* bit zero -> control panel is installed */
gestaltDesktopPicturesInstalled = 0,
/* bit one -> a picture is currently displayed */
gestaltDesktopPicturesDisplayed = 1
}
- Desktop Pictures supports the following image file formats:
'PICT', QuickTime Compressed 'PICT',
picture clippings, and files supported by QuickTime 2.5 graphics
import components including JPEG, GIF, and Photoshop.
- Optional default alignment and positioning information for
picture files can be stored in the picture file's resource fork by
applications creating picture files. The 'dkpx' ID 0 resource
containing this information is formatted as two long words. The
first long word contains the positioning information (tiled=1,
centered/actual size=2, scaled=3, fill screen=4) and the second
long word contains either zero or some combination of the possible
alignment flags (left = 0x10, right = 0x20, top = 0x40, bottom =
0x80). When present, Desktop Pictures will use this information as
a hint from the picture creator about how the picture ought to
appear by default. Users can, of course, reconfigure these
settings. For example, to set the default Desktop Pictures display
settings for a picture as 'original size, aligned with the top
right corner of the screen', the picture's associated
'dkpx' ID 0 resource would contain the following (in
hex): 0x00000002 and 0x00000060.
- If Desktop Pictures is installed and cannot find its
preferences file during startup, it looks for a picture file in
the System Folder called "Desktop Picture", and uses it as the
picture for the main screen. Users can remove or replace this
picture using the control panel.
- The utility patterns feature of the Desktop Patterns control
panel is not supported by the Desktop Pictures control panel (In
Mac OS 7.5.x and 7.6.x, holding down the option key in the Desktop
Patterns control panel would allow you to set the pattern used in utilities such as Calculator or Key Caps).
|
Compatibility Note:
The first time Desktop Pictures runs, it reads in any
existing Desktop Patterns from the Desktop Patterns control
panel's preferences file (if this file exists in the
Preferences folder). After saving the original patterns in it's
own preferences file, Desktop Pictures moves the old
preferences file to the trash.
|

|
Extensions Manager 4.0.1
|
The new Extensions Manager control panel provides user
interface facilities for users to configure components of the system
software that are installed at system startup time. The following
have been corrected in the Extensions Manager control panel:
- CCI resources may now have any resource ID. Each file
may have only one.
- CCI resources are now recognized in control panels.
Related Materials:
- Technote TN1091, "Extensions
Manager 4.0"

|
File Sharing 8.0
|
This control panel allows for the configuration of
various settings related to sharing files and linking applications
over a network. The new File Sharing control panel replaces both the
older Sharing Setup and File Sharing Monitor control panels. The new
File Sharing control panel has the following features:
- Packaged as an
'APPC' type application file (can
be a target for AppleScript ).
- Supports a suite of AppleScript commands and is also
recordable. AppleScript commands related to file sharing, formerly
supported by the Finder, are now supported by the File Sharing
control panel. The File Sharing control panel provides scripting
support for starting and stopping shared services, querying server
status, and manipulating connected users and shared items.
- Added support for turning on AppleTalk when starting file
sharing.
- Third-party extensions and applications can query the current
status of either the File Sharing control panel or the Users &
Groups control panel by using the following Gestalt selector:
enum {
/* the 'fsue' selector is installed by the File Sharing INIT */
gestaltFileSharingAttr = 'fsue',
/* bit zero -> File Sharing control panel is installed */
gestaltFileSharingCPPresent = 0,
/* bit one -> Users & Groups control panel is installed */
gestaltUsersAndGroupsCPPresent = 1
}
- In Mac OS 8, the set of file sharing permissions have been
reduced to "Read and Write", "Read Only", "Write Only", and
"None". When encountering sharing information created with System
7.x, the System 7 permissions are mapped to Mac OS 8 permissions
as follows:
|
System 7.x Privileges
|
Mac OS 8 Privileges
|
|
See Folders
|
See Files
|
Make Changes
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Read & Write
|
|
X
|
X
|
|
Read Only
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
Write Only (Drop Box)*
|
|
X
|
|
X
|
Write Only (Drop Box)*
|
|
X
|
|
|
None*
|
|
|
X
|
|
None*
|
|
|
|
X
|
Write Only (Drop Box)
|
|
|
|
|
None
|
*These entries cannot be mapped accurately to the new set of
access privileges. In these cases, the permissions are mapped to
the most conservative permission corresponding to the original
setting.
- Additional AppleScript support for file sharing is provided by
the FileSharing Commands scripting addition which duplicates the
most commonly used scripting support found in both the File
Sharing control panel and the Users and Groups control panel. This
scripting addition is provided so scripts are not required to
launch the control panels to access File Sharing services. For
security reasons, many of the commands found in the FileSharing
Commands scripting addition cannot be used remotely (via scripts
run on a different machines across a network). To use remote
scripts for these operations, remove the FileSharing Commands file
from the "Scripting Additions" folder and enable remote program
linking for the appropriate control panel.

|
General Controls 7.7
|
The General Controls control panel has been revised to
support the new Appearance guidelines in
both itself and the shutdown dialog.

|
Keyboard 8.0
|
- The Keyboard control panel provides user interface services for
configuring the keyboard menu (displayed when more than one
keyboard layout is selected in the Keyboard control panel) and
adjusting various settings for the computer's keyboard.
- The Keyboard control panel is now packaged as an
'APPC' file and, as such, it can be a target for
AppleScript.
- Additional AppleScript support for keyboard options is
provided by the Keyboard scripting addition. This scripting
addition is provided so scripts are not required to launch the
Keyboard control panel to access Keyboard services.
- The Keyboard control panel no longer calls
SetScriptVariable to update the default
'KCHR'. This is handled by the keyboard menu.
- New for this version of the Keyboard control panel is the
ability to configure the keyboard menu to display various selected
layouts for different input methods (multi-byte scripts are not
displayed by in the keyboard menu). Under System 7, users could
select a keyboard layout in the Keyboard control panel for the
currently active input method for a multi-byte system, but that
information was neither transferred to the input method nor read
by the input method preferences, and, therefore, there was no
effect. All multi-byte input methods are now displayed in the
keyboard menu.
- Keyboard layout lists are displayed in the control panel by
choosing the appropriate script from the script pop-up menu. The
user can select multiple layouts and her selection is reflected in
the keyboard menu, grouped for each script. Users now select their
active layout from the keyboard menu. In the System 7 Keyboard
control panel, users had no way of knowing that they had to switch
the script with a keyboard shortcut or with the keyboard menu to
see the list of keyboard layouts for the other scripts. Note that
changing the script via the menu or a keyboard shortcut will
not update the list any more or change the chosen script in
the popup menu.
- The Keyboard control panel writes to a preferences file which
contains a resource of type
'kcfg'. The layout of
this resource is:
// an entry in the resource format
struct ConfigEntry {
SInt16 kchrID;
UInt16 flags;
};
typedef struct ConfigEntry ConfigEntry;
typedef ConfigEntry *ConfigEntryPtr;
// the resource format
struct KCHRConfig {
SInt32 version;
ConfigEntry kchrTable[kVariableLengthArray];
};
typedef struct KCHRConfig KCHRConfig;
typedef KCHRConfig *KCHRConfigPtr, **KCHRConfigHandle;
// bit numbers for the flags field
enum {
kKCHRInMenu = 1,
kDefaultKCHR = 2,
kKCHRValid = 4
};
- The Keyboard control panel only writes the
kKCHRInMenu bit-flag to the resource. The Script
Manager sets the other bits.
- The Keyboard control panel needs certain information from a
resource of type
'STR#' in the System file, to help
with localization. 'STR#' ID -20291 in the system
file will hold the following:
- The name of the preferences file.
- The file type of the preferences file.
- The creator code of the preferences file.
- The type of resource to look for.
- The file type of the Keyboard control panel.
- The creator code of the Keyboard control panel.
- The Keyboard control panel uses the Apple platinum
Appearance.
- The Keyboard control panel has Apple
Guide support, with an Apple Guide button for quick online
keyboard-related help.

|
Location Manager 1.0.2
|
Apple Location Manager is a toolbox extension that
allows mobile users to save and restore sets of configurations
("locations") under a single name. For example, a user can define a
group of printers, network settings, and extension sets for multiple
locations.
ALM is developer-extensible. Apple Location Manager modules appear
in the "Location Manager Modules" folder in the System Folder.
Version 1.0.2 has been updated to be compatible with new features
in Mac OS 8.
Related Materials:

|
Mac OS Easy Open
|
Mac OS Easy Open is a optional component of the
operating system providing translation services for users opening
documents in one application that have been created by other
applications.
- Version 9.0 of the MacLinkPlus translators are shipped with
Mac OS 8. This version of MacLinkPlus includes additional
utilities, online help, and facilities for contacting the creators
of MacLinkPlus for technical support.
Related Materials:

|
Memory 7.5.8
|
The Memory control panel provides user interface
facilities for the configuration of virtual memory, RAM disk storage,
and the size of the disk cache.
- The new Memory control panel has been revised to support the
new Apple platinum Appearance.

|
Monitors & Sound 1.3
|
The Monitors & Sound control panel originally
provided user interface services for configuring and adjusting
various settings for AppleVision monitors attached to the computer.
In addition, the Monitors & Sound control panel now provides
services formerly provided by the Monitors control panel and the
Sound control panel.
- A problem that sometimes prevented the AppleVision extension
from loading at system startup has been corrected.
|
Compatibility Note:
On systems where a video or sound device cannot be accessed
using the Monitors & Sound control panel, use the Monitors
control panel or the Sound control panel instead. These older
control panels are installed in the Apple Extras folder in the
root directory. Unless these older control panels are
specifically required, the new unified Monitors & Sound
control panel should be used.
|

|
Startup Disk 7.6.1
|
The Startup Disk control panel provides user interface
facilities for choosing the disk that will be used to run the
computer the next time it starts up.
- This version of Startup Disk provides some corrections in its
implementation and changes in the user interface to comply with
the new Appearance guidelines.

|
Users and Groups 8.0
|
This control panel provides facilities for the
specification and configuration of user names and passwords for
people who are able to establish network connections with the
computer. The following changes are present in the Users and Groups
control panel:
- It is now packaged as an
'APPC' type file.
- The new Users and Groups control panel supports a suite of
AppleScript commands. It is also
recordable. For additional information regarding using AppleScript
for with the Users and Groups control panel, refer to the
File Sharing control panel section.
- Third party extensions and applications can query the current
status of either the File Sharing control panel or the Users &
Groups control panel by using the following
Gestalt
selector:
enum {
/* the 'fsue' selector is installed by the File Sharing INIT */
gestaltFileSharingAttr = 'fsue',
/* bit zero -> File Sharing control panel is installed */
gestaltFileSharingCPPresent = 0,
/* bit one -> Users & Groups control panel is installed */
gestaltUsersAndGroupsCPPresent = 1
}

|
Web Sharing 1.1
|
Web Sharing provides facilities for users to configure
and set up the "Web Sharing" folder on their computer to act as a
World Wide Web site. Web Sharing allows users to publish documents on
an intranet or the Internet. Documents placed in the Web Sharing
folder will be available to other users by using means of any web
browsers available on any platform. Web Sharing provides the
following facilities:
- Support for HTTP 2.2.
- WebStar 1.3 compliance.
- Supports access control configurable using the standard File
Sharing facilities.
- Compatible with either MacTCP 2.0.6 or OpenTransport.
- Full CGI support.
- Runs as a background application allowing up to eight
simultaneous connections.
|
Note:
Web Sharing is not recommended for use on computers
connected to the Internet via PPP. It is intended for use on
computers that have a static internet address.
|
Related Materials:

|
System Extensions
|
System extensions are located in the Extensions folder
inside the System Folder. For a system extension to be active, it
must be located in the Extensions folder when the system starts up.
Extensions are not loaded if the shift key is held down while the
system is starting up.

|
Appearance Extension 1.0
|
The Appearance Extension implements the Appearance
Manager, which extends the facilities provided by the Control
Manager, the Dialog Manager, the Menu Manager, and the Window Manager
to provide the Apple platinum Appearance to existing and new
graphical elements of the Mac OS environment.
|
IMPORTANT:
The Appearance Extension will be loaded at
system startup if it is in the Extensions (Disabled) folder. Mac OS 8
will not boot if this file is removed from the System Folder
hierarchy.
|
Appearance Manager introduces several extensions to the toolbox
APIs. Developers should refer to the Appearance Manager documentation
and SDK regarding these new API's for further details.
Related Materials:

|
Apple CD-ROM 5.4
|
The Apple CD-ROM driver contains some enhancements for
support of new Apple products and corrects some problems found in
previous versions of the driver.
- Contains both the ATAPI and the SCSI CD-ROM drivers.
- Supports mounting and reading of the following CD formats:
- HFS
- ISO 9660
- PhotoCD
- Video CD
- CD Extra
- CD-XA Mode 1 and 2
- CD-I Mode 1 and 2
- Audio CD.
|
Compatibility Note:
Non-Apple CD drives are no longer supported by the Apple
CD-ROM driver.
|
Related Materials:
- Technote
DV18,
"CD-ROM Notes (Most Excellent)"

|
Apple Guide 2.2.1
|
Apple Guide provides system-wide instructional online
help services for nearly every aspect of the Mac OS user experience.
It is extensible in many ways so developers are able to provide Guide
help files for their own applications and utilities. This release of
Apple Guide delivers speed improvements and corrections over previous
versions. Changes and notes of interest to developers are as follows:
- The help key (or Command-?) can be used to access the help
services. The help key will no longer launch Apple Guide if any
modifier key besides the mouse button or the caps lock key is
down. This change allows developers to use the help key in
combination with modifier keys to deliver help content that
supplements Apple Guide.
- Apple Guide's list management routines have been improved to
handle more than the previous limit of 350 items.
- If an application calls
Gestalt using the
'help' selector and Apple Guide has been moved out of
the Extensions folder, then selector will indicate that Apple
Guide is not installed. Several applications and control panels
were not checking for unresolved weak links to the Apple Guide
API, and would crash.
- Implemented the AGFile library as a shared library for both
PowerPC and CFM-68K.
- Increasing application heap size allows for more
OpenDoc and modular help files, and it
improves Apple Guide's ability to play larger QuickTime movies.
Related Materials:

|
AppleScript 1.1.2
|
AppleScript is a component of the operating system
that provides a scripting interface for users to automate actions
that would normally require use of the menus and keyboard, but even
more importantly allows users to access functionality of applications
which would be difficult or impossible to access by hand. As
described below, this new version of AppleScript includes some
corrections and enhancements that improve its operation with Mac OS
8.
Special enhancements for Mac OS 8:
- The Scripting Additions folder located in the System Folder is
automatically searched by AppleScript for scripting additions. The
old location, the Scripting Additions folder in the Extensions
folder, is still searched for additions; however, developers
installing additions should begin using the
Folder Manager to determine the
correct placement.
- The dialog boxes for AppleScript and the Display Dialog
scripting additions now include 'dlg' and 'al' resources to
give them the new Apple platinum
Appearance when running on a Mac OS 8
machine.
- The AppleScript component now includes a 'CCI
 ' resource
describing its function for display in the Extensions Manager
control panel. ' resource
describing its function for display in the Extensions Manager
control panel.
- The 'File Commands' scripting addition's 'Path To' command now
accepts the following new parameters that can be used to specify
the additional folders defined in the Mac OS 8 implementation of
the FindFolder routine:
- "desktop applications", "desktop applications folder"
- "application support", "application support folder"
- "control strip modules", "control strip modules folder"
- "desktop documents", "desktop documents folder"
- "editors", "editors folder"
- "help", "help folder"
- "modem scripts", "modem scripts folder"
- "plug-ins", "internet plug-ins, "internet plug-ins folder"
- "printer descriptions", "printer descriptions folder"
- "printer drivers", "printer drivers folder"
- "scripting additions," "scripting additions folder"
- "shared libraries", "shared libraries folder"
- "stationery", "stationery folder"
- "shutdown items", "shutdown items folder"
- "voices", "voices folder"
|
Note:
These keywords return an error at runtime if executed on
a version of Mac OS earlier than Mac OS 8.
|
Other Enhancements:
- A resource has been changed in the Script Editor to give an
additional half inch of left margin on printouts to accommodate
3-hole punching.
- When the Event Log exceeds 20,000 characters, excess
characters are now lost off the top to make room for new events
and results. This eliminates the -20013 error that occurred on
logging many repetitive, long, or ongoing processes.
- Repeatedly doing a Save As to an applet tended to accumulate
multiple resources of type PREC and others, because
Ad was being called regardless of whether
that resource already existed. This has been fixed in Script
Editor 1.1.2.
- AppleScript 1.1.2 will now find and launch files of type
'APPL', 'APPC', 'APPD', or
'appe' with either 'CODE' or
'cfrg' resources, plus the Finder. These file types
may be used as targets for AppleScripts.
- The AppleScript symbol table in version 1.1.1 and earlier
accommodated a maximum of 1,024 symbols. In version 1.1.2 this is
expanded to 4,096 symbols.
Corrections:
- Concatenating a record with an empty vector, e.g. {a:1, b:2}
& {}, caused a crash in version 1.1.1. This is fixed in 1.1.2.
- Execution of an applet caused, under certain conditions,
memory location $0006 to be overwritten, causing incompatibility
problems with specific third party applications. Applets that are
reopened and saved with AppleScript 1.1.2 will no longer overwrite
this address.
- Multiple-character text item delimiters caused the machine to
hang in an infinite loop on operations like "count text items of"
and "text item 2 of". This has been fixed in AppleScript 1.1.2.
- In AppleScript 1.1.1, the test to see whether a script could
be reloaded into memory was faulty, and would not allow loading of
scripts that had been created and saved under identical
circumstances. This has been fixed in 1.1.2.
- Certain numbers (such as 1310.4) cannot be represented with
full accuracy as floating point numbers. AppleScript 1.1.1 was
displaying these numbers with too much precision, so compilation
and dec of "1310.4" returned "1310.400000000001". An
attempt has been made to fix some of these cases in AppleScript
1.1.2, and efforts are being made to remove this problem
altogether in AppleScript 1.2. NOTE that this change in behavior
may break some scripts that relied on the inaccurate numbers
returned by AppleScript 1.1.1, or require precision beyond the
12th significant digit.
- The method of locking handles holding scripting addition data
was not suited for re-entrance. This has been fixed in 1.1.2, so
that a scripting addition may be called while it is being called
by another process.
- The English syntax for AppleScript required the possessive
property form (for example: "AppleScript's version") to be
lower-case. AppleScript 1.1.2 allows an uppercase S (for example:
"APPLESCRIPT'S VERSION"), to be accepted. It also supports
case-insensitivity for "DOESN'T".
- In AppleScript 1.1.1, the bytecode Program Counter for the
runtime engine was left uninitialized, and a routine to set its
new value calculated the offset between the new value and the old.
In machines with >768Mb of memory, this offset overflowed a
30-bit signed integer and resulted in a numeric overflow error,
preventing anything from being compiled. The program counter is
now initialized to 0, and the offset is not calculated when the PC
is 0, so this error should not happen in AppleScript 1.1.2 and
later.
- The month property of a date type should be one of {January,
February...} Setting this to a number mistakenly resulted in a
Stack Overflow error. In 1.1.2 it results in a more normal "Can't
make <number> into the expected type" error result.
- Quitting the Script Editor, then canceling the quit, caused a
crash, because the data structures for the Results and Log windows
were already disposed. This has been fixed in Script Editor 1.1.2.
Related Materials:

|
AppleShare Workstation Client 3.7.1
|
AppleShare Workstation Client provides file sharing
services for the Finder and applications on Mac OS-compatible
computers networked with file servers.
- A problem where a "File Server unexpectedly closed down"
message would appear after a restart has been corrected.
- AppleShare Client 3.7 provides facilities for TCP/IP connections
to AppleShare IP 5.0 servers.
Related Materials:
|
Compatibility Note:
AppleShare Workstation Client 3.7.1 can be used with
versions of Mac OS including 7.5.3 and later.
|

|
Color Picker 2.1
|
The Color Picker Extension provides standard user
interface facilities for selecting colors. The new ColorPicker offers
the following new features and corrections:
- Native (in fact, "fat") pickers have been implemented.
- Additional pickers have been added (Crayon and CMYK),
- Has been updated to provide ColorSync 2 support, if it is
installed. Older versions of the Color Picker only supported
ColorSync 1.
- The New 'EyeDropper' tool allows users to 'pick up' colors
displayed in the foreground application's windows while the picker
window is visible and the option key is held down.
- Some problems related to saving and restoring the active
resource chain when Color Picker is called have been corrected.
- Under some conditions, the "more choices" list did not show
any pickers.
- The interface file
<ColorPicker.h> has been
revised as several calls are no longer used.
|
Compatibility Note:
ColorPicker 2.1 is compatible with System 7.5 and later.
|

|
Contextual Menu Extension 1.0
|
This extension implements the Contextual Menu Manager.
Contextual Menus is a new element of the Mac OS user interface
experience providing menus associating a set of relevant commands
with a particular location on the screen. Contextual menus are
activated by a control-click.
Finder 8 utilizes the facilities provided by the Contextual Menu
Manager.
Related Materials:
- The
Menu
Manager chapter of Inside Macintosh: Macintosh Toolbox
Essentials.

|
FireWire 1.0
|
FireWire 1.0 is Apple's Mac OS support for the IEEE
1394 High Performance Serial Bus standard. This extension adds
services to the Mac OS that support the use of third-party FireWire
hardware and software.
Mac OS 8 ships with the FireWire 1.0 extension.

|
Mac OS Runtime for Java 1.0.2
|
Mac OS Runtime for Java (MRJ) is Apple's
implementation of the Java runtime environment. MRJ allows Java
functionality to be embedded in Mac OS applications, and applications
using MRJ's JManager API are able to run Java applets and
applications.
The Mac OS 8 installation ships with MRJ 1.0.2.
Related Materials:

|
OpenDoc 1.2.1 1.2.1
|
OpenDoc is the Mac OS implementation of the OpenDoc
open, multi-platform architecture for component software.
The Mac OS 8 installation ships with OpenDoc 1.2.1.
Related Materials:

|
Open Transport 1.2
|
OpenTransport is the only supported networking
technology for Mac OS 8.
Open Transport 1.2 is installed with Mac OS 8.
Some important changes and enhancements in OpenTransport 1.2
include:
- Includes CFM-68K implementations of its libraries.
- Correctly handles 'ping' packets larger than 65536 bytes in
answer to the Ping
'o Death problem.
- A memory problem that could occur when Open Transport was
being used at the same time as ARA Multi-port Client software has
been corrected.
- A problem where, under certain conditions, Open Transport was
not unloading and reloading some of its libraries correctly has
been corrected.
- Addresses the "SYN flood" denial of service events issue.
- Tuned to obsolete the OTSlowLinkTuneUp.
- Improved compatibility between the native implementation of
PAP and some third party printers.
- Corrections in the native ADSP implementation.
- Corrects problems that could occur in AppleShare servers under
a heavy load.
For more information about changes, corrections, and new
features present in Open Transport 1.2, developers should consult
the OpenTransport release notes and Developer notes found in the
OpenTransport SDK.
Related Materials:

|
Open Transport/PPP 1.0.1
|
Open Transport/PPP provides Point to Point Protocol
connection services for users connecting to the internet via modem.
- Mac OS 8 ships with Open Transport/PPP 1.0.1.
|
Compatibility Note:
Open Transport/PPP configuration information is stored in
the file "Remote Access Connections" in the folder "...System
Folder:Preferences:Remote Access:". Users transferring
configuration files from older system installations will want
to copy this file.
|
|
Warning:
ARA Client 2.1 must not be installed over the Open
Transport/PPP (OT/PPP) installation included with Mac OS 8.
Installing the ARA Client 2.1 after installing OT/PPP will
replace the OT/PPP Modem Files which can cause connection
problems for Open Transport/PPP. However, it is perfectly safe
to install OT/PPP after having installed the ARA Client 2.1.
|
Related Materials:

|
QuickTime 2.5
|
QuickTime provides various multimedia services for the
Mac OS including the ability to display movies and facilities for the
translation and display of various audio and visual data file
formats.
- QuickTime 2.5 is installed with Mac OS 8.0.
Related Materials:

|
QuickTime MPEG Extension 1.0
|
This extension provides MPEG media handling services
for QuickTime.
- The QuickTime MPEG Extension is installed with Mac OS
8.0.
|
|
QuickTime Musical Instruments Extension 2.5
|
This extension provides a selection of musical
instrument synthesizers available for use in QuickTime.
- The QuickTime Musical Instruments 2.5 is installed with
Mac OS 8.0.
|

|
QuickTime VR 2.0
|
QuickTimeVR provides standard components and API entry
points usable for the display and management of virtual reality
panoramas.
- The QuickTime VR Extension 2.0.1 is installed with Mac
OS 8.0.
Related Materials:
|
|
QuickDraw 3D 1.5 1
|
QuickDraw 3D provides 3D drawing services for the Mac
OS.
- Mac OS 8.0 ships with QuickDraw 3D 1.5 1.
Related Materials:

|
QuickDraw GX 1.1.6
|
QuickDraw GX provides advanced graphics and
typographic services for the Mac OS.
- The Mac OS 8 installation ships with QuickDraw GX 1.1.6.
- ColorSync is no longer installed with QuickDraw GX, since it
is installed with Mac OS 8.
|
Compatibility Note:
GX printing and GX printer drivers are no longer supported
in Mac OS 8. GX Printing or older versions of GX will be
removed during installation.
|
Related Materials:

|
Speech Manager 1.5
|
The Speech Manager provides services for the
translation of text into audible speech.
- Mac OS 8 installation ships with English Text to Speech 1.5.
Related Materials:

|
Text Encoding Converter 1.2
|
The Text Encoding Converter enables the conversion of text data
from one encoding to another (e.g. Mac OS Roman to Windows
Latin-1). It is targeted for Internet applications which need to
handle text typically provided in non-Mac OS encodings. It also
represents the first step for supporting Unicode on Mac OS.
Features include:
Apple Extras

|
Cyberdog 2.0
|
Cyberdog is an application and a set of
OpenDoc components which provide access to
Internet and intranet services including the World Wide Web, email,
file servers, and more. Updated software developer packages and
documents describing Cyberdog features available to developers are
available at the Cyberdog web site.
- Mac OS 8 installation ships with Cyberdog 2.0.
- Cyberdog 2.0 is "fat" and utilizes CFM-68K on 68040 machines.

|
Apple Remote Access Client 2.1
|
The Apple Remote Access (ARA) Client allows users to
dial in and connect to AppleTalk networks from remote locations.
Mac OS 8 ships with Apple Remote Access Client 2.1.
|
Warning:
ARA Client 2.1 must not be installed over the Open
Transport/PPP (OT/PPP) installation included with Mac OS 8.
Installing the ARA Client 2.1 after installing OT/PPP will
replace the OT/PPP Modem Files which can cause connection
problems for Open Transport/PPP. However, it is perfectly safe
to install OT/PPP after having installed the ARA Client 2.1.
|
Related Materials:
- The Apple Remote Access API SDK
- The Apple Remote Access Modem SDK

|
Assistants
|
The Assistants folder, located at the root level on
the system disk, contains assistant applications used to assist the
user in configuring software.

|
Mac OS Setup Assistant 1.0
|
Mac OS Setup Assistant is an addition to the Mac OS
installation/startup user experience designed to unify the various
options and preferences, making system configuration easier by
presenting these options in the form of an interview. During
installation, an alias to the Mac OS Setup Assistant application is
placed inside the Startup Items folder so that it will launch the
first time the Mac OS is booted after a Mac OS installation. This
alias is deleted once Mac OS Setup Assistant is run for the fist
time. The assistant helps the user through several aspects of
configuration, all of which can be accomplished (or overridden)
through various control panels and standard system configuration
dialogs.
The following is a list of the areas Mac OS Setup Assistant
configures:
- Regional Preferences: keyboard layout, date/time/number
format, and script sorting (Keyboard, Date & Time, Numbers,
and Text control panels). This panel only appears if multiple
preferences are available for the default system script. These
changes take effect when the panel is exited and will not revert
to previous settings if the interview is cut short.
- Name and Organization: File Sharing control panel and Internet
Config extension user name, Internet Config user organization.
- Time and Date: Daylight Savings Time, Time, and Date (Date
& Time control panel). These changes take effect immediately
and will not revert to previous settings if the interview is cut
short.
- Geographic Location: Time Zone (Date & Time or Map control
panel). If the location selected is a US or Canadian city the
standard Apple printer drivers are set to use US Letter as the
default paper size, otherwise A4 is set to be the default paper
size. Default UMich, Info-Mac, and Anarchie servers are entered in
InternetConfig.
- Finder Preferences: Simple Finder (Finder Preferences dialog).
- Computer Name and Password: File Sharing computer name and
owner password (File Sharing control panel).
- Shared Folder: turn on AppleTalk and File Sharing, create a
folder on the desktop with full guest access privileges (File
Sharing, Users & Groups control panels, and Finder).
- Printer Selection/Printer Type: these panels only display
printers supported by the Finder Desktop Printers extension. To
find the network printers, the assistant searches each available
AppleTalk port, starting with the default port, until one or more
supported printers are found. If network printers are found on any
port other than the default, AppleTalk is redirected to that port.
With the exception of Regional Preferences and Date/Time/DST,
no changes are made until the user selects "Go Ahead" at the end
of the interview. Any port change made during the network printer
search is undone if the user quits the assistant prior to
selecting "Go Ahead". If AppleTalk is turned on during the
interview but no AppleTalk dependent options are selected in the
interview, AppleTalk will be turned off after the interview is
completed and serial port connections will be unaffected.
Apple Developer Utilities
Mac OS 8 requires updated copies of the following
Apple Developer Utilities:

|
MacsBug 6.5.4
|
MacsBug is Apple's low level debugger providing
interface facilities for the disassembly and perusal of assembler and
machine level instructions.
|
Note:
MacsBug 6.5.4 or later should be used with Mac OS 8.
Versions of MacsBug earlier than 6.5.4 will not work with Mac
OS 8.
|
Related Materials:

|
System Picker 1.1
|
|
System Picker is an Apple utility providing facilities
for switching the active system between different system folders
installed on a Mac OS compatible computer.
- System Picker 1.0.1 does not work with Mac OS 8. System Picker
1.1 or later should be used instead.
- System Picker 1.1 allows system folders to be selected by
dragging and dropping their icon into System Picker's icon.
Related Materials:
Items no longer supported
Color control panel
The Color control panel has been removed from the
control panels folder as its functionality has been replaced by the
Appearance control panel.
Desktop Patterns control panel
The Desktop Patterns control panel has been removed
from the control panels folder as its functionality has been replaced
by the Desktop Pictures control panel.
The utility patterns feature of the Desktop Patterns control panel is
no longer supported ( In Mac OS 7.5.x and 7.6.x holding down the
option key in the Desktop Patterns control panel would allow you to
set the pattern used in utilities such as the Calculator desk
accessory, or the Key Caps utility, et al.).
File Sharing Monitor control panel
Functionality formerly found in this control panel has
been moved to the File Sharing control
panel.
Finder Extensions
Files known as "Finder Extensions" are no longer
supported. These items include: the Network Extension, the Clipping
Extension, the Catalogs Extension, the Mailbox Extension, the Mail
Folders Extension, the Finder Scripting Extension, the PC Card
Extension, and the Desktop Printer Extension. The functionality found
in most of these extensions has been built directly into the new
Finder.
QuickDraw GX Printing
QuickDraw GX Printing is no longer supported. No GX
Printer drivers or printing extensions will work with Mac OS 8.
Labels control panel
The Labels control panel has been removed. Its
functionality has been incorporated into the preferences dialog in
Finder.
Sharing Setup control panel
Functionality formerly found in this control panel has
been moved to the File Sharing control
panel.
Views control panel
The Views control panel has been removed. Its
functionality has been incorporated into the new "Finder Preferences"
and "View Options" dialogs in Finder.
Window Shade control panel
The Window Shade control panel has been removed. Its
functionality has been incorporated into the Appearance Manager.
Configuration facilities formerly provided by this control panel are
now provided by the Appearance control
panel.
|
Change History
|
29-Mar-1999
|
Updated and expanded the
details and samples presented for Apple
Event Changes in the Finder
8.0 section.
|
|
6-Aug-1998
|
Fixed broken Apple Location Manager and Appearance Manager SDK links.
|
|
11-Dec-1997
|
Fixed broken links in the QuickDraw
GX section. Corrected the 'fntb' drag flavor
description in the Finder:New Drag
Flavors section ('Preventing Folders from Springing Open' was
changed to 'Disabling Finder Tracking Behavior'). And
XFInfo spelling changed to FXInfo.
|
|
6-Nov-1997
|
1.3 Documented a crashing bug with
UTVolCacheWriteIP under in the File
System Manager section.
|
|
6-Oct-1997
|
1.2 New HideOnSwitch flag defined along with it's accessor
routines, GetHideOnSwitch and
SetHideOnSwitch, in the Process
Manager section. |
|
11-Sep-1997
|
1.1 QTVR version changed to 2.0.1, added information about the
flavorNotSaved flag in the Finder:New Drag Flavors section, added
"Cleanup at Startup" folder to Folder Manager section with
developer note about its use.
|
Back to top
Downloadables
|

|
Acrobat version of this Note (404 K).
|
Download
|
|